How To Make A Cnc Drawing Machine At Home
Introduction
This projection is a continuation of the version 1 of the Drawing Automobile I built a year ago. The previous Cartoon Motorcar I build was based on T-Bot design. It had some disadvantages like information technology was heavy, cantilever-like design which gave information technology a swinging activeness that used to distort the cartoon, and information technology was slow. So I decided to make some improvements in version two.
https://www.arnabkumardas.com/cnc.html

Project Beak of Material
Click on Each Product Below and You will be Taken to the Product Folio that I trust and take used in my Projection. I Highly Recommend You Buy Directly from the Link Below or Add together to Cart.
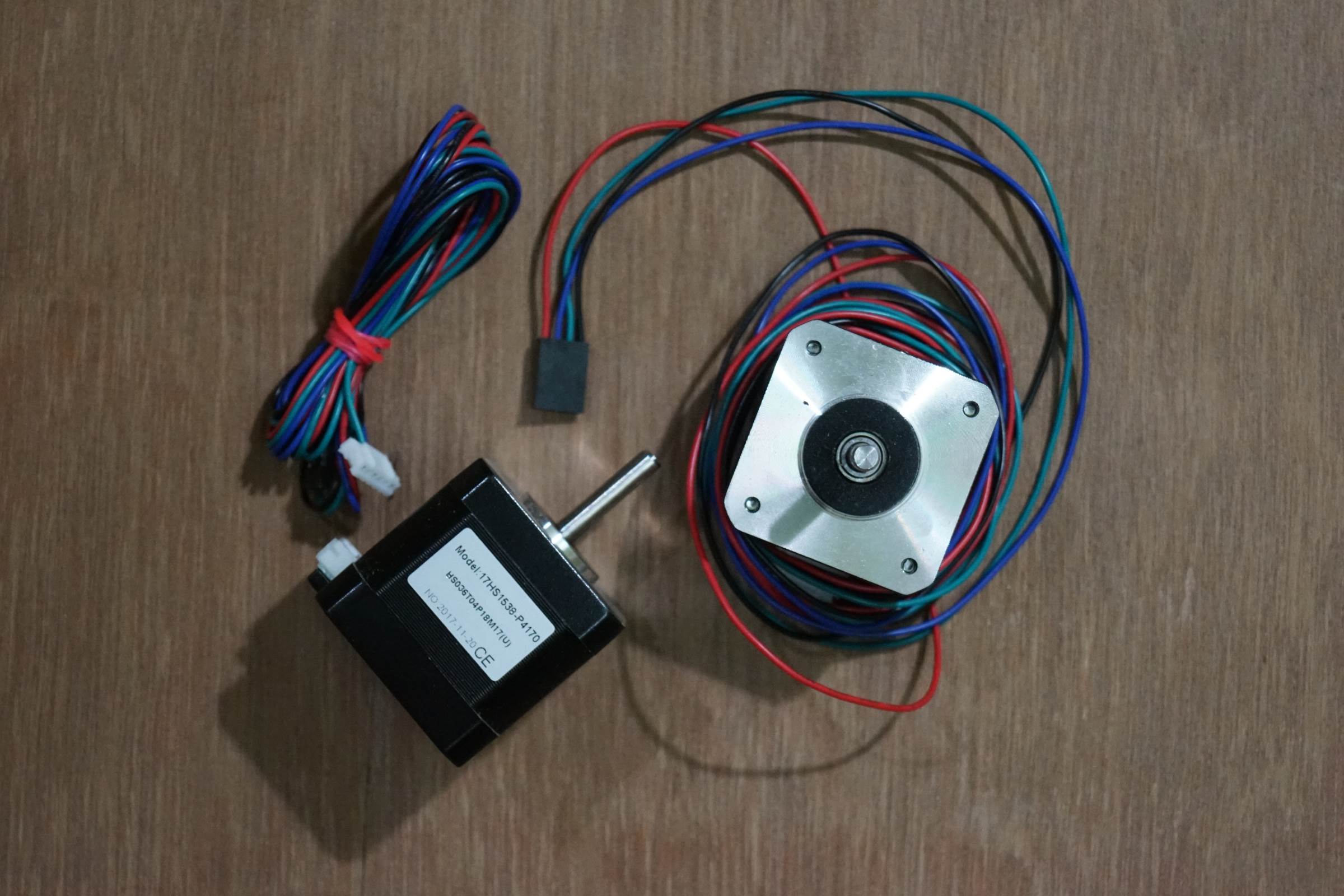
• 2 x NEMA 17 Steppers 1.8 Caste Step 12v Torque more than 4kg/cm
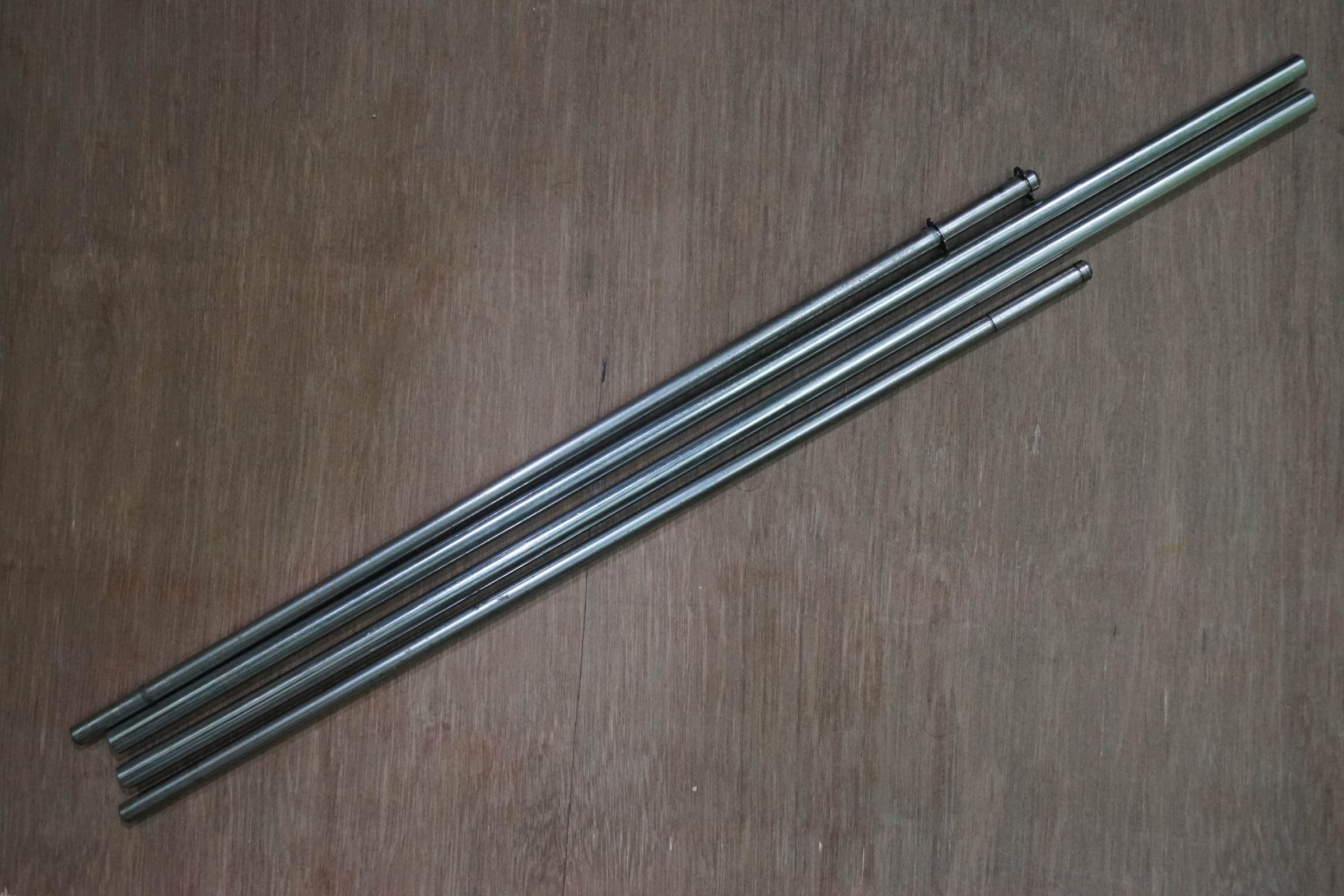
• 2 x 8mm Stainless Steel Shine Rods
• 2 ten 10mm Stainless Steel Smooth Rods
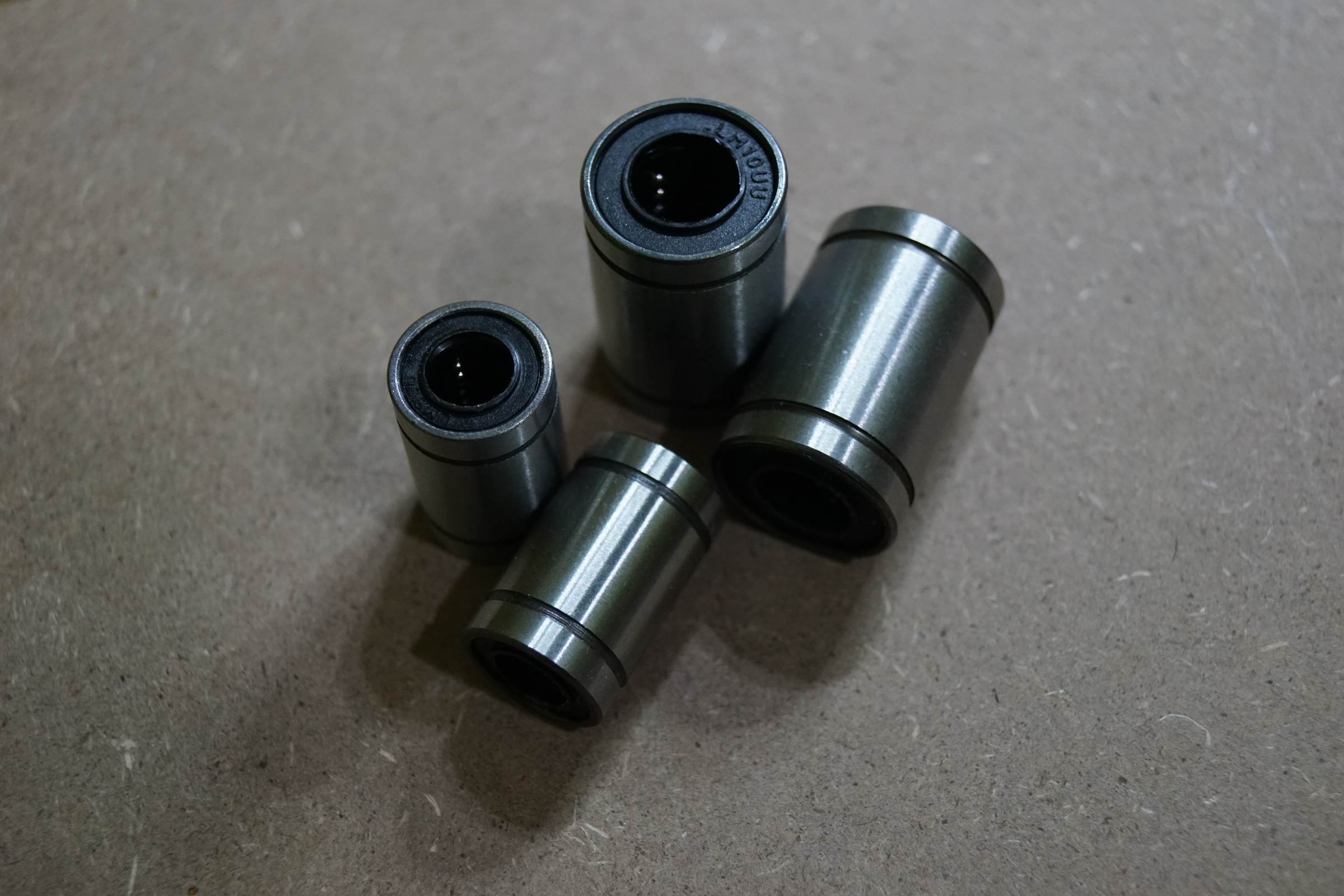
• 2 x LM8UU 8mm Linear Bearing or SC8UU 8mm Linear Bearing
• 4 x SK8 8mm Rod End Support
• 4 x LM10UU 10mm Linear Bearing or SC10UU 10mm Linear Bearing
• 2 x SK10 10mm Rod End Back up
• 2 ten xx-Tooth GT2 pulleys
• 12 x F623ZZ Bearings
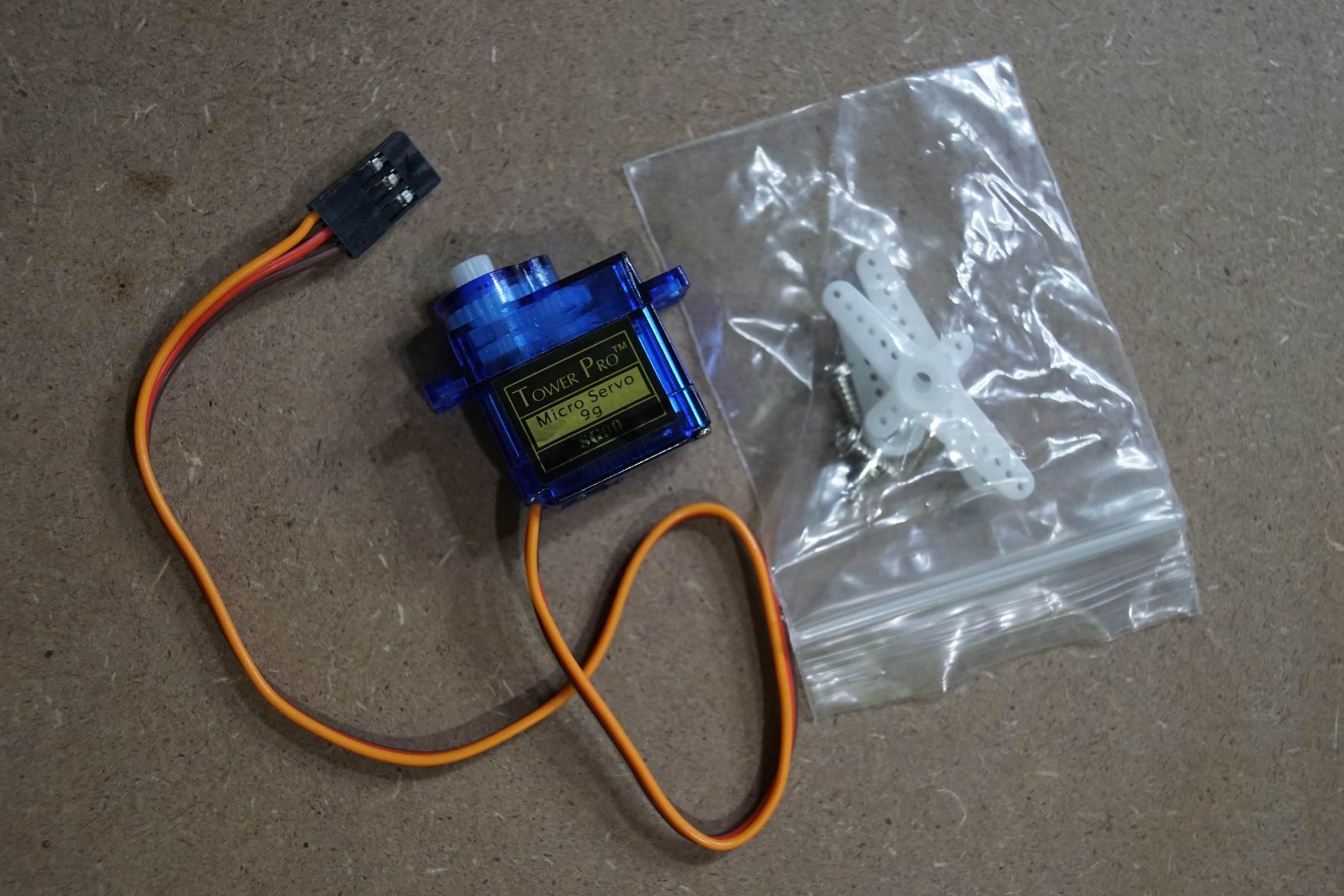
• 1 x Micro Servo SG90
• 1 10 Arduino UNO
• one ten CNC Shield V3
• 2 ten Pololu Step Sticks A4988 Stepper Driver
• 1 x GT2 Belt (3 meters long)
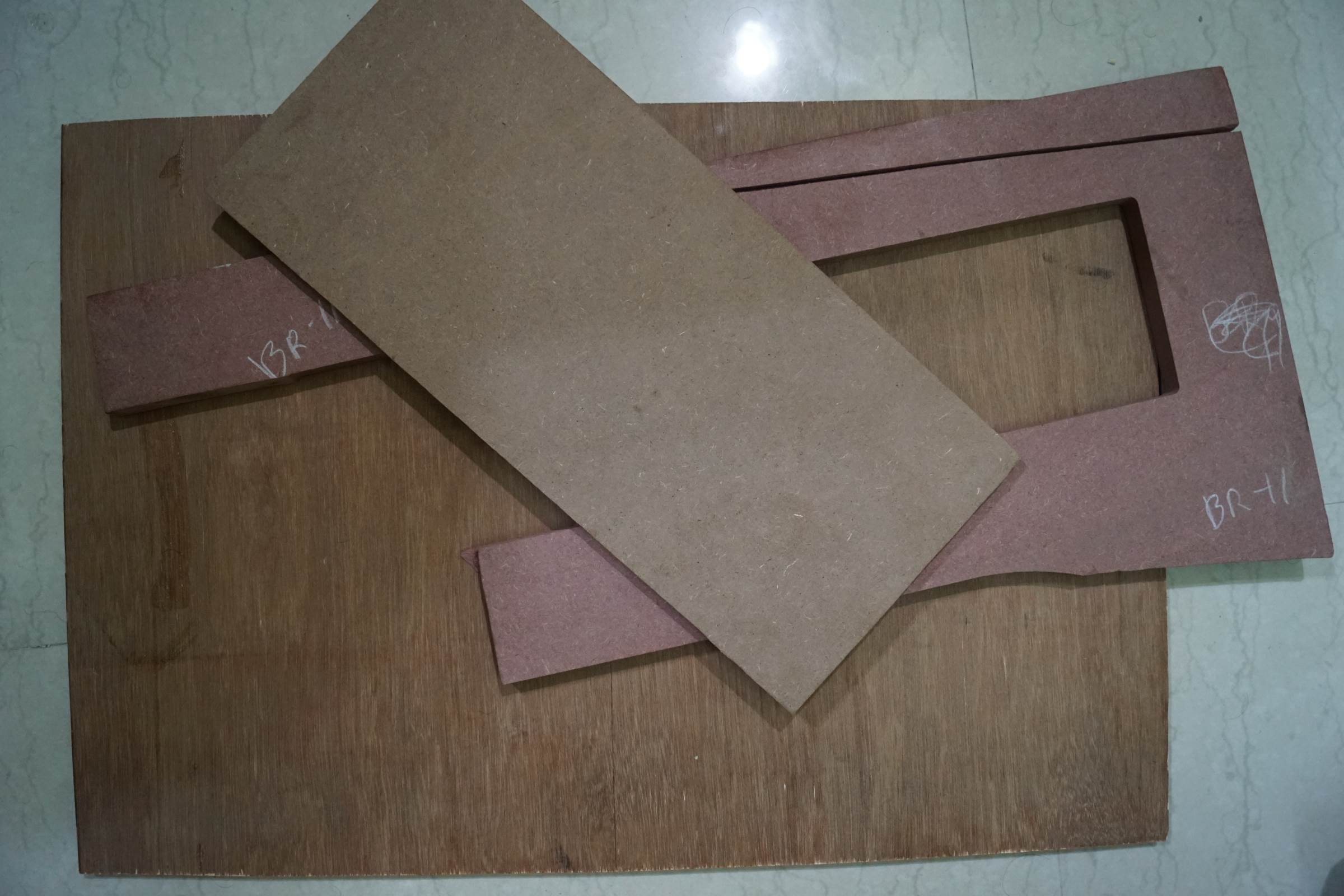
• one 10 Hard Wood Ply 50cmx60cmx1.5cm
• Multiple screws with nuts
• 1 x Wire 5m
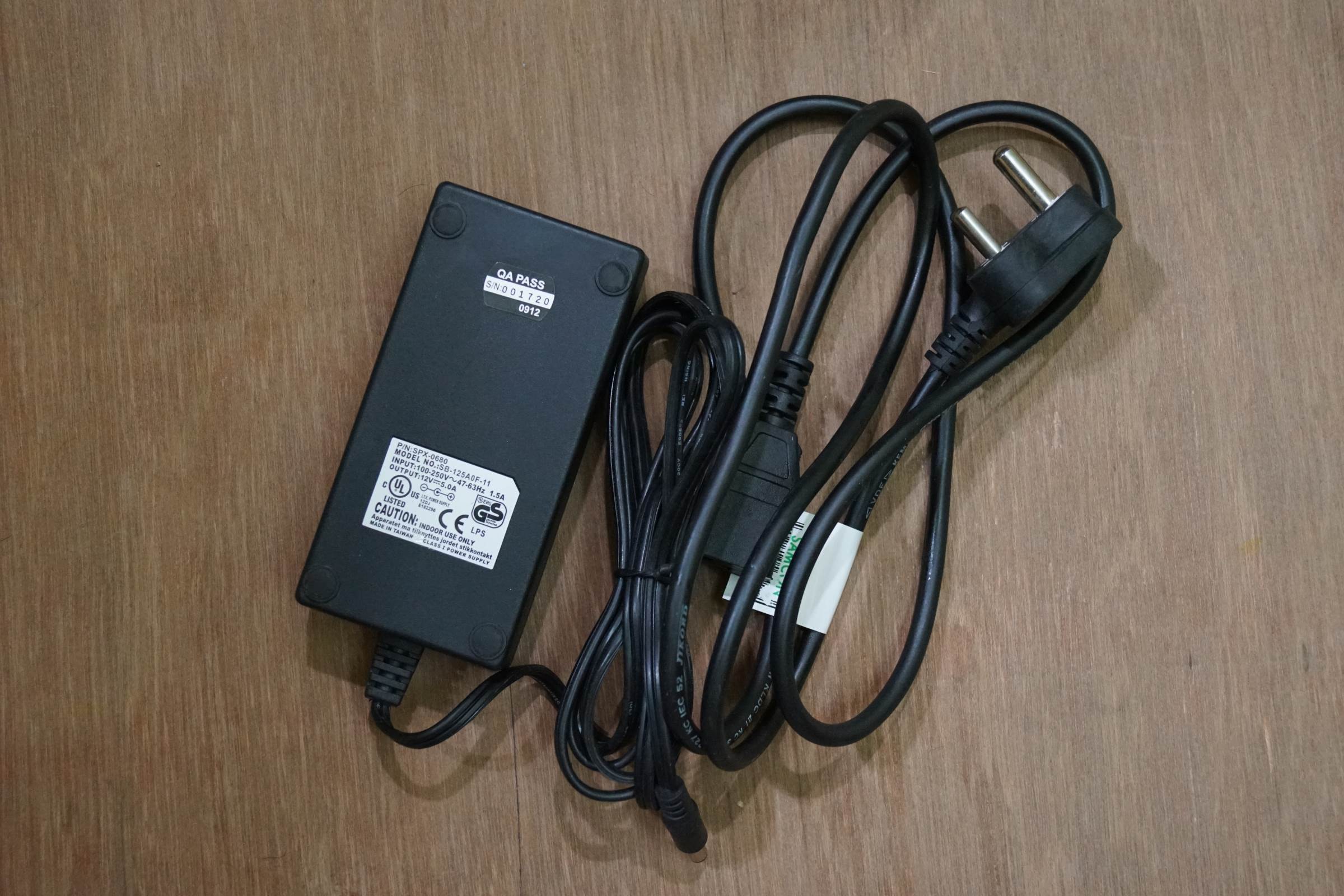
• 1 x SMPS 12v 5A
• 1 10 Soldering Wire
• 1 x Solder
• one x Jig Saw
• 1 10 Jig Saw Blade for wood cut
• 1 x USB Wire
• 4 ten Special Liquid ink PEN of multiple colours
• Miscellaneous Tools and Components
H-Bot Mechanics
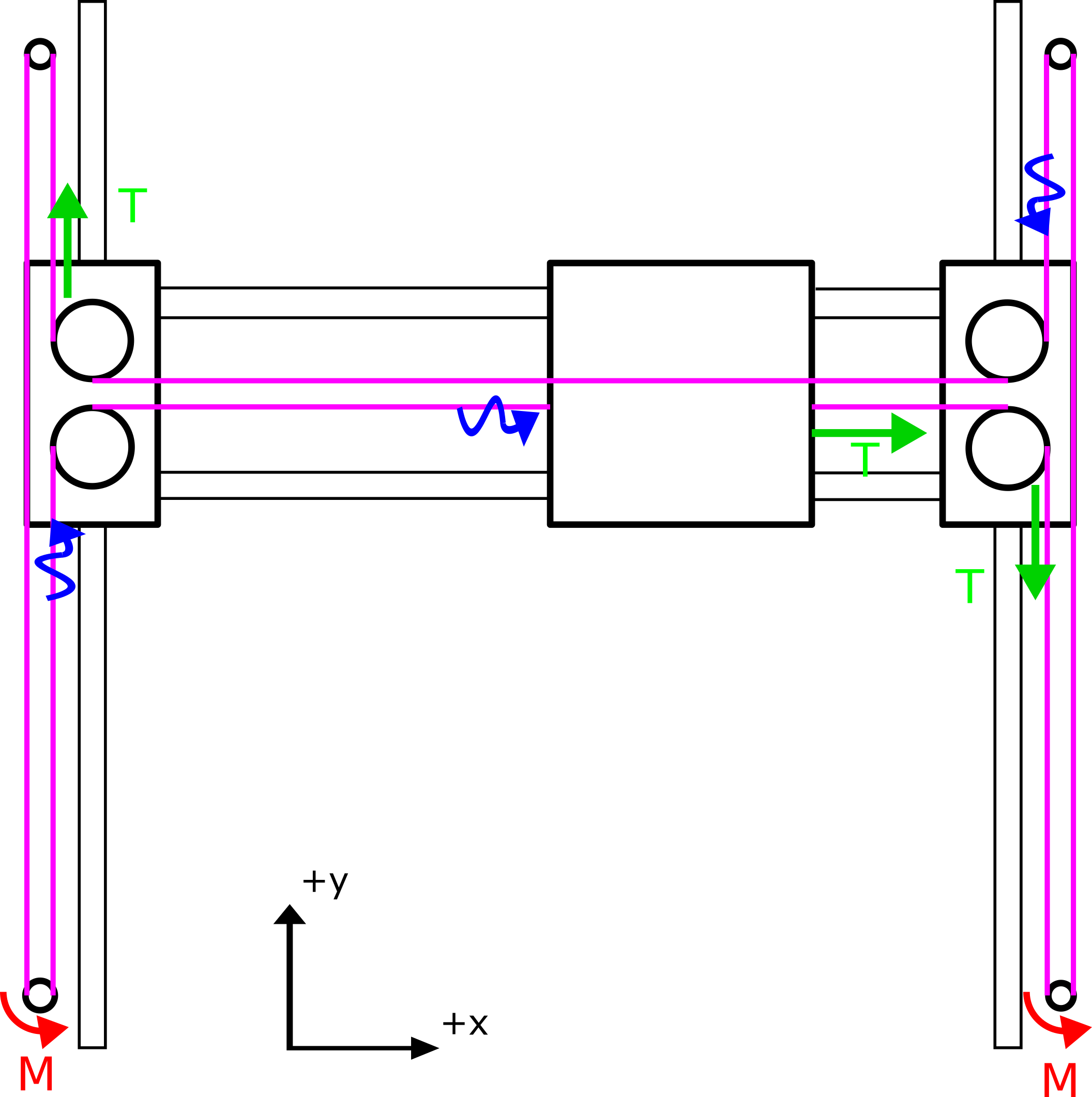
Why H-Bot? Considering it has few advantages that made me choose it. It is cheap to construct as it needs less bearings and other materials, simple, clean and
Construction
Time needed:2 days.
Steps for building the Arduino Drawing Machine
- 50cm x 60cm Ply Wood for Drawing Machne's Base of operations

- 17HS1538 Stepper Motor

- Micro Servo Motor 9G

- 12V 5A SMPS Power Supply

- LM10UU and LM8UU Linear Bearing

- 8mm and 10mm Stainless Steel SS Smooth Rods

- MDF Board for other Parts

- Grid Paper for pasting on Ply Wood and MDF Boards for easy cutting

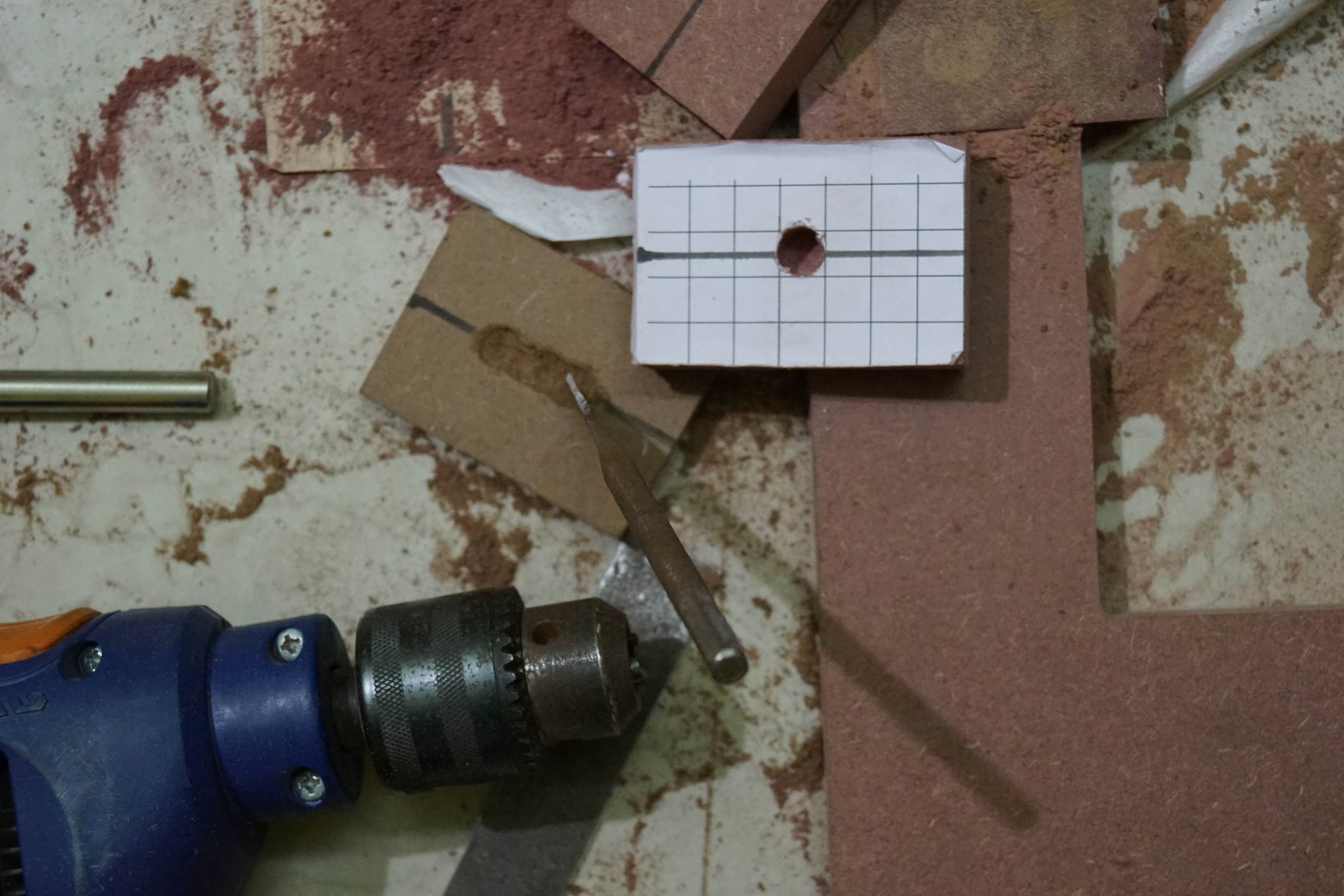
- Mockup to finalize position earlier drilling holes / cut

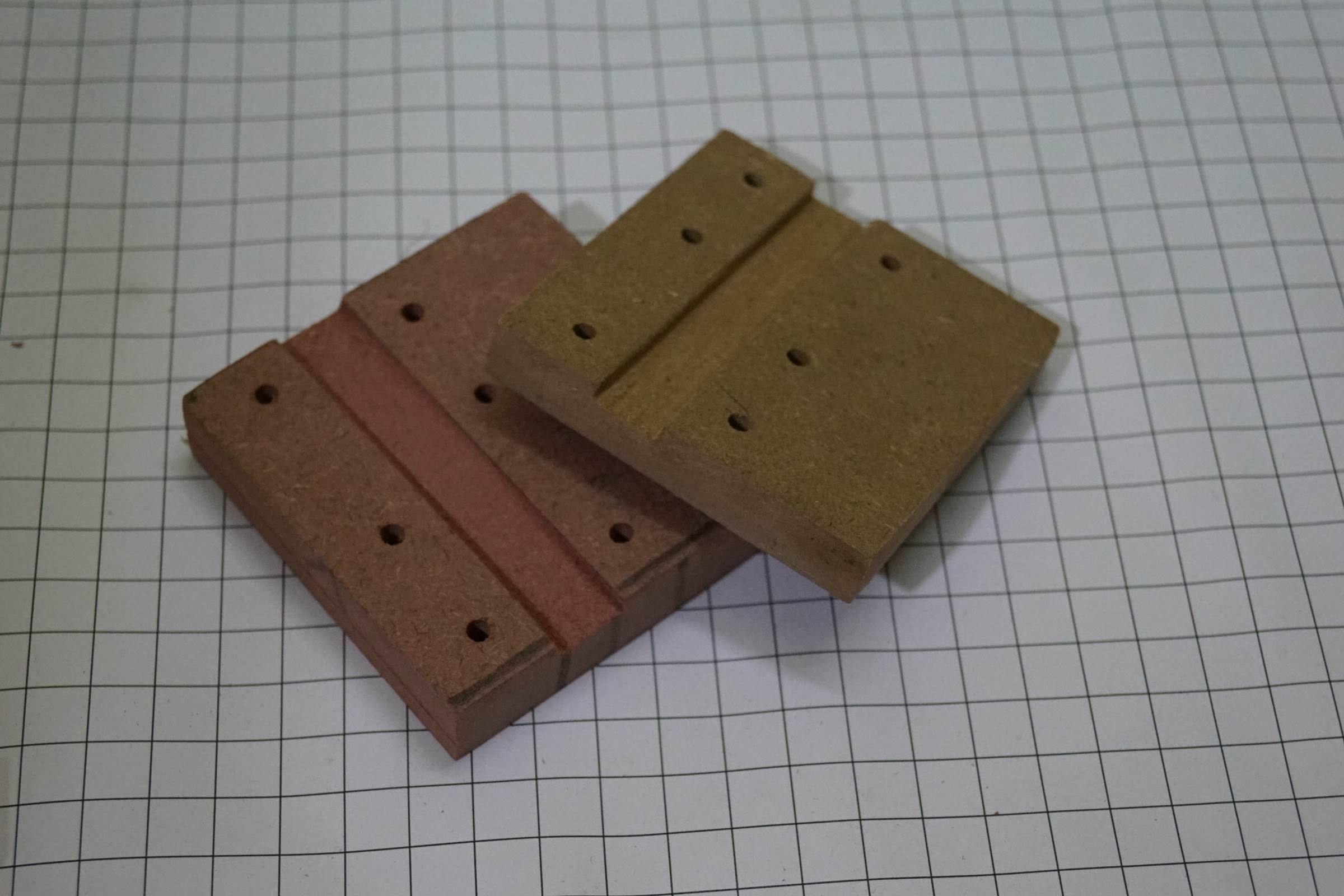
- Small pieces of MDF Board covered with Grid Newspaper for Axes Joints and Linear Bearing Holder

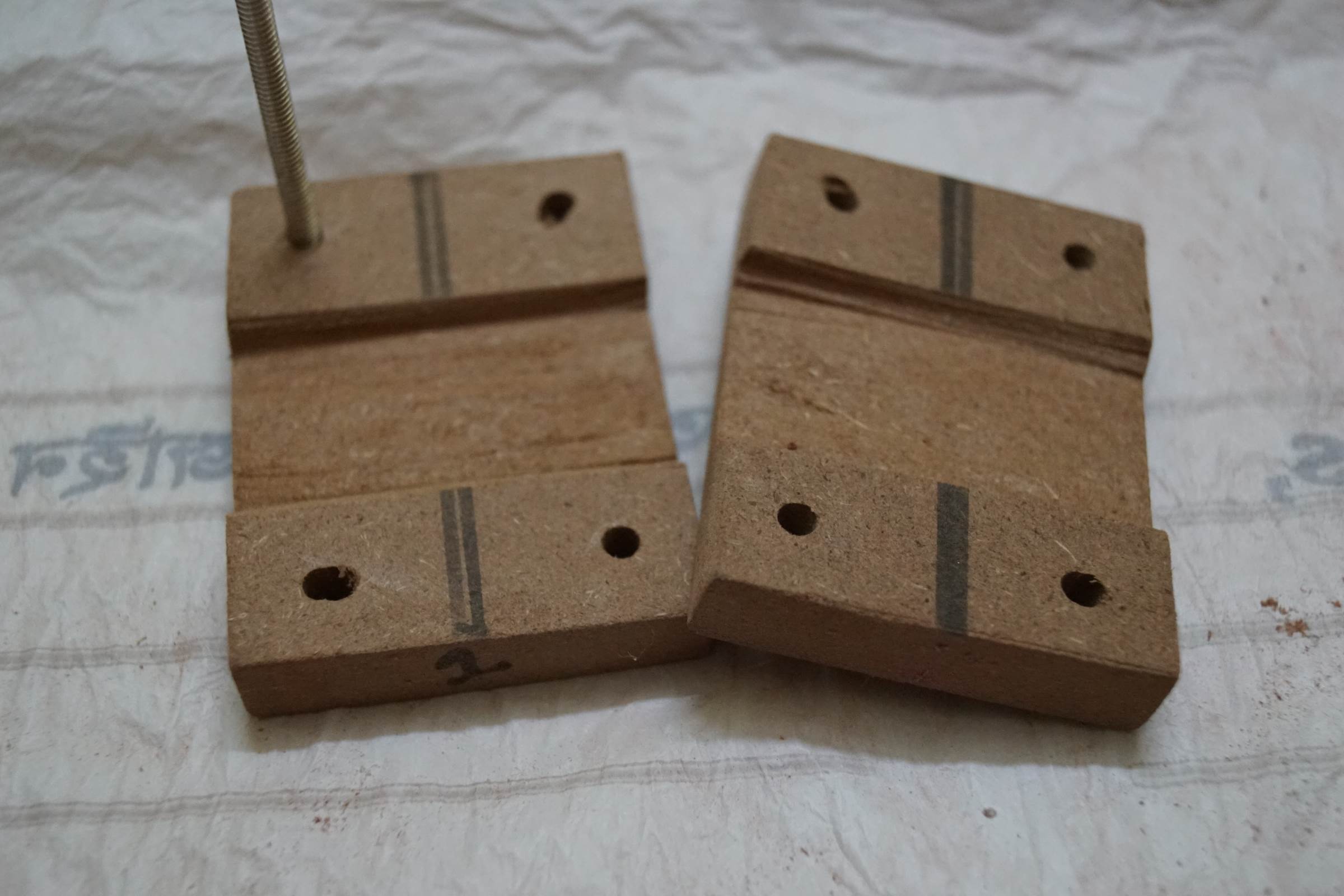
- 10mm Half Depth Drill was done on four pieces of MDF Lath on
same point to make them end support for the two Y-Centrality 10mm rods
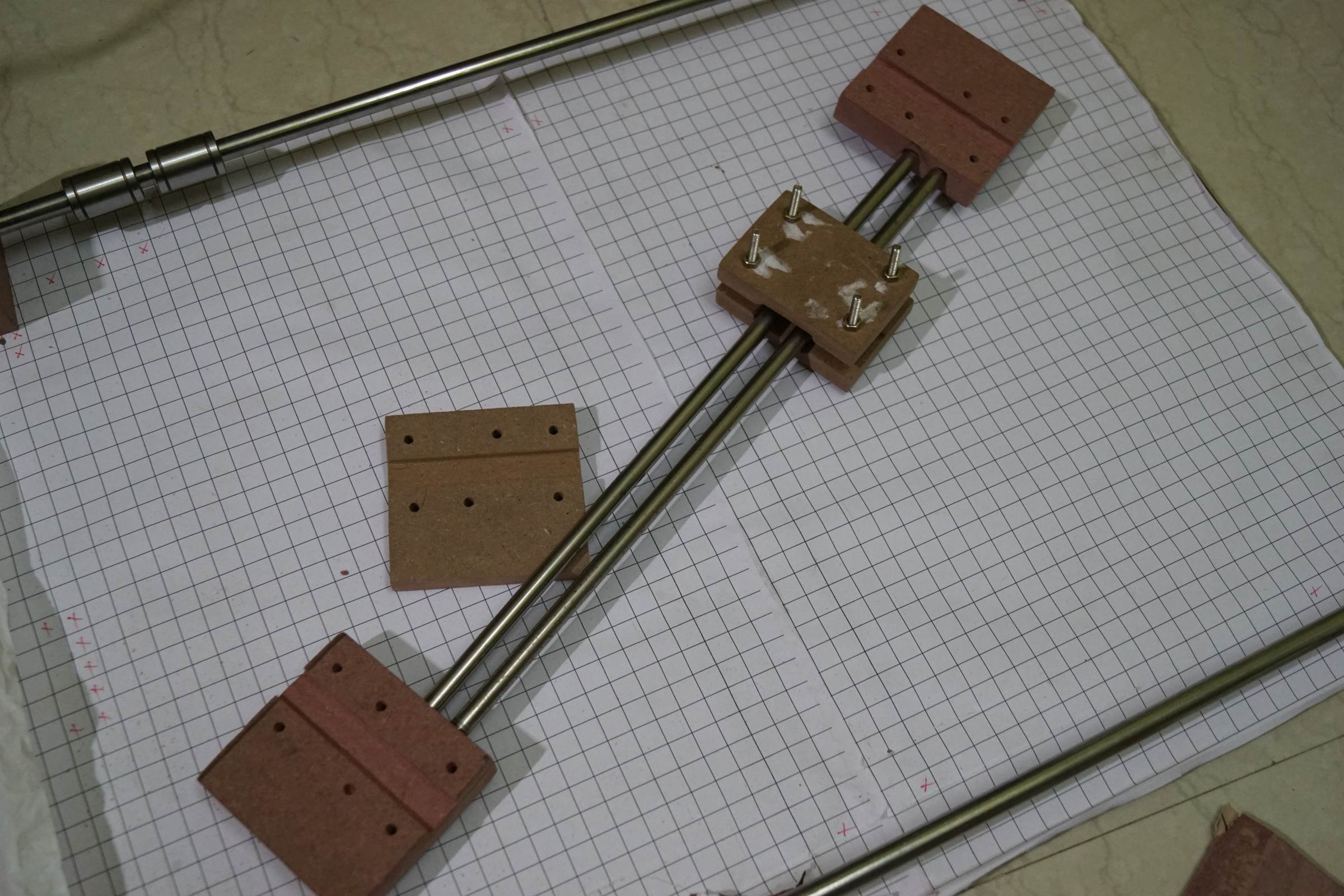
- Finish Support for 10mm Y Axis rod

- X-Axis Finish Plates with a depression to support the LM10UU Linear Begetting of Y-Axis

- X-Axis Heart Carriage Plates with a depression to support the LM8UU Linear Bearing of X-Centrality

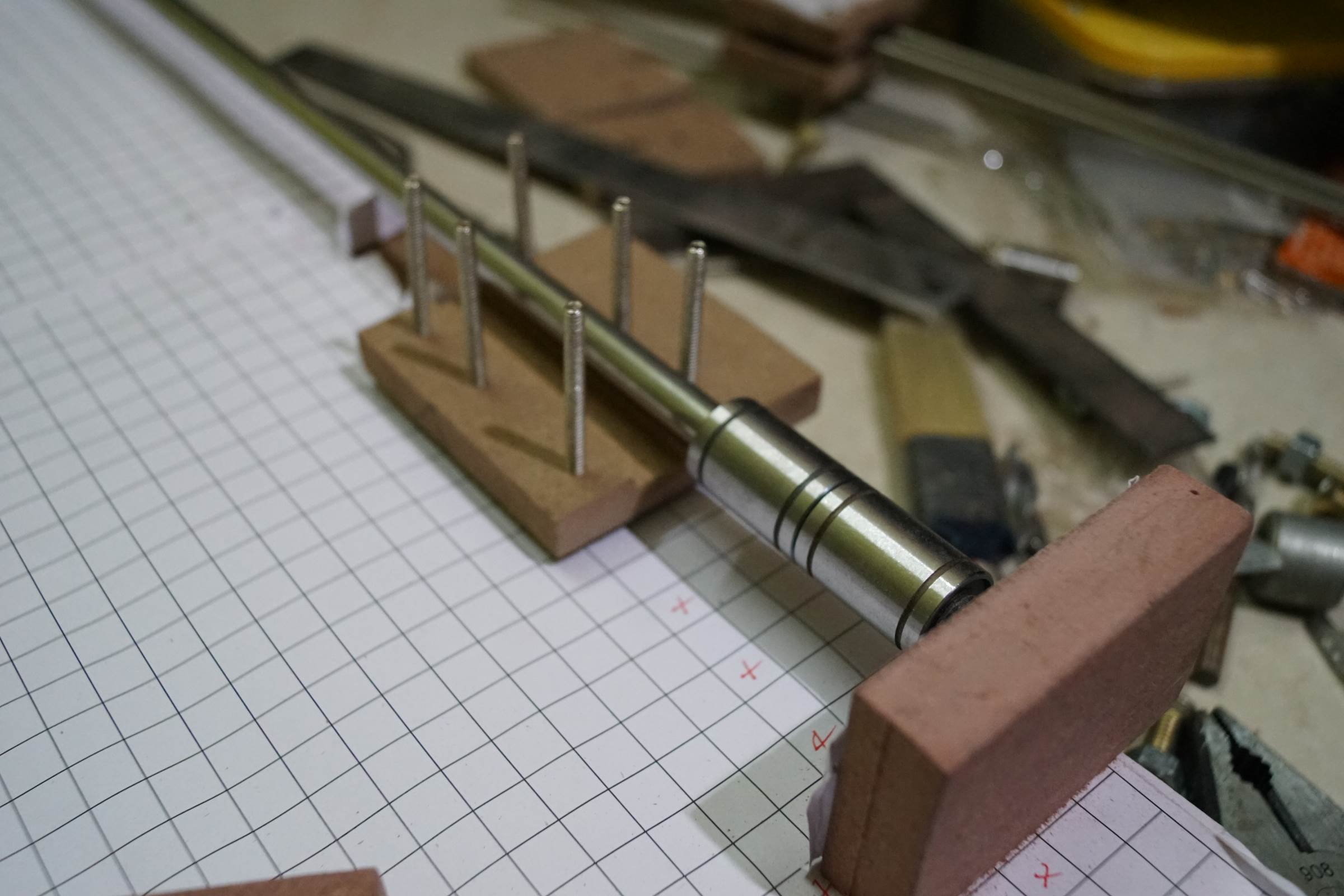
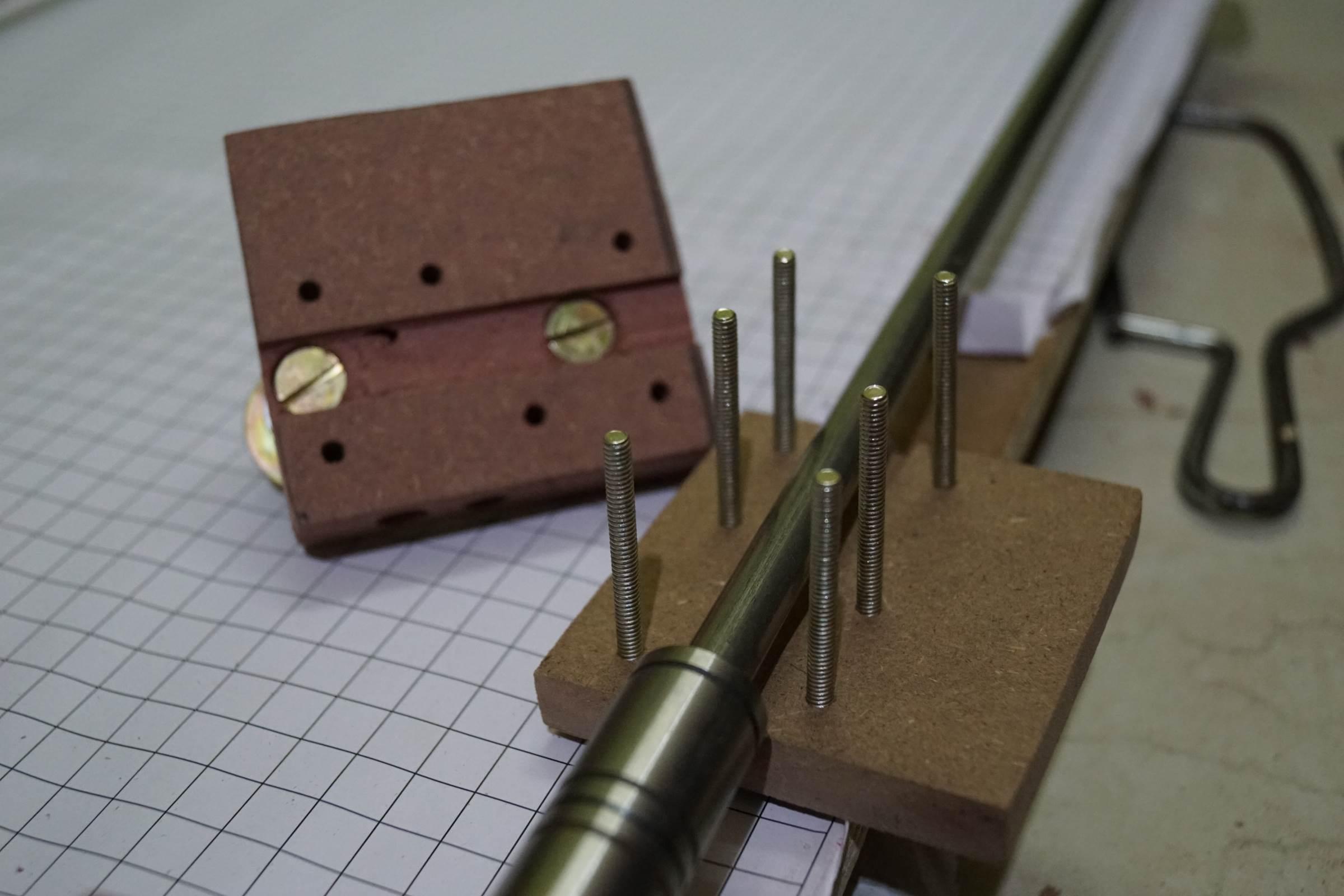
- Assembelled X-Axis of Arduino Drawing Machine, End Plates of the X-Axis were horizontal 8mm drilled to support two 10-Axis rods

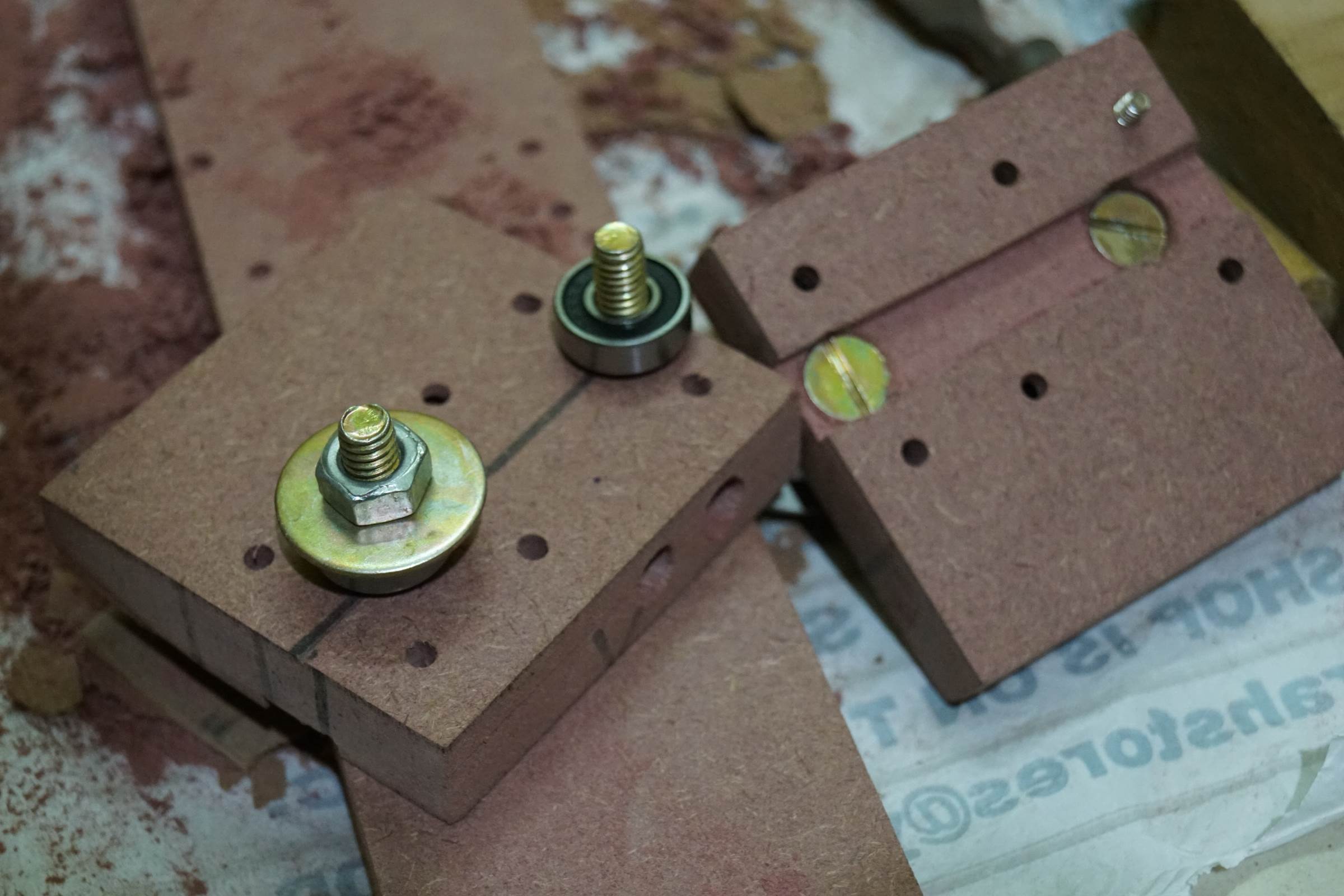
- Each X-Centrality' Upper-Terminate Plates were drilled and bearings were attached on nut, bolt and washer to work like a pulley for the chugalug

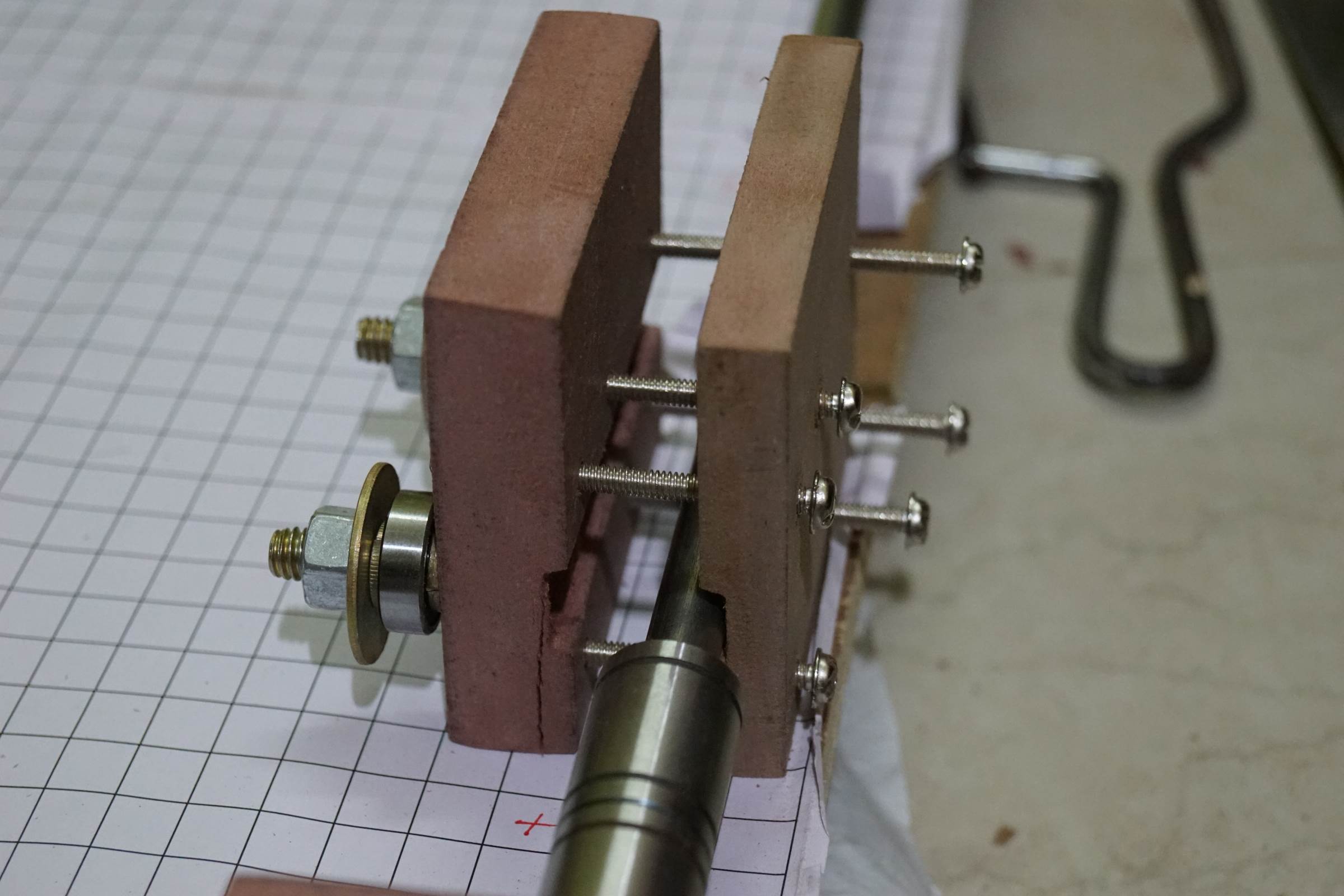
- Assembling the X Centrality End Holders

- Assembling the Ten Centrality End Holders

- Assembling the X Axis End Holders

- Chugalug Assembly of Arduino Cartoon Robot
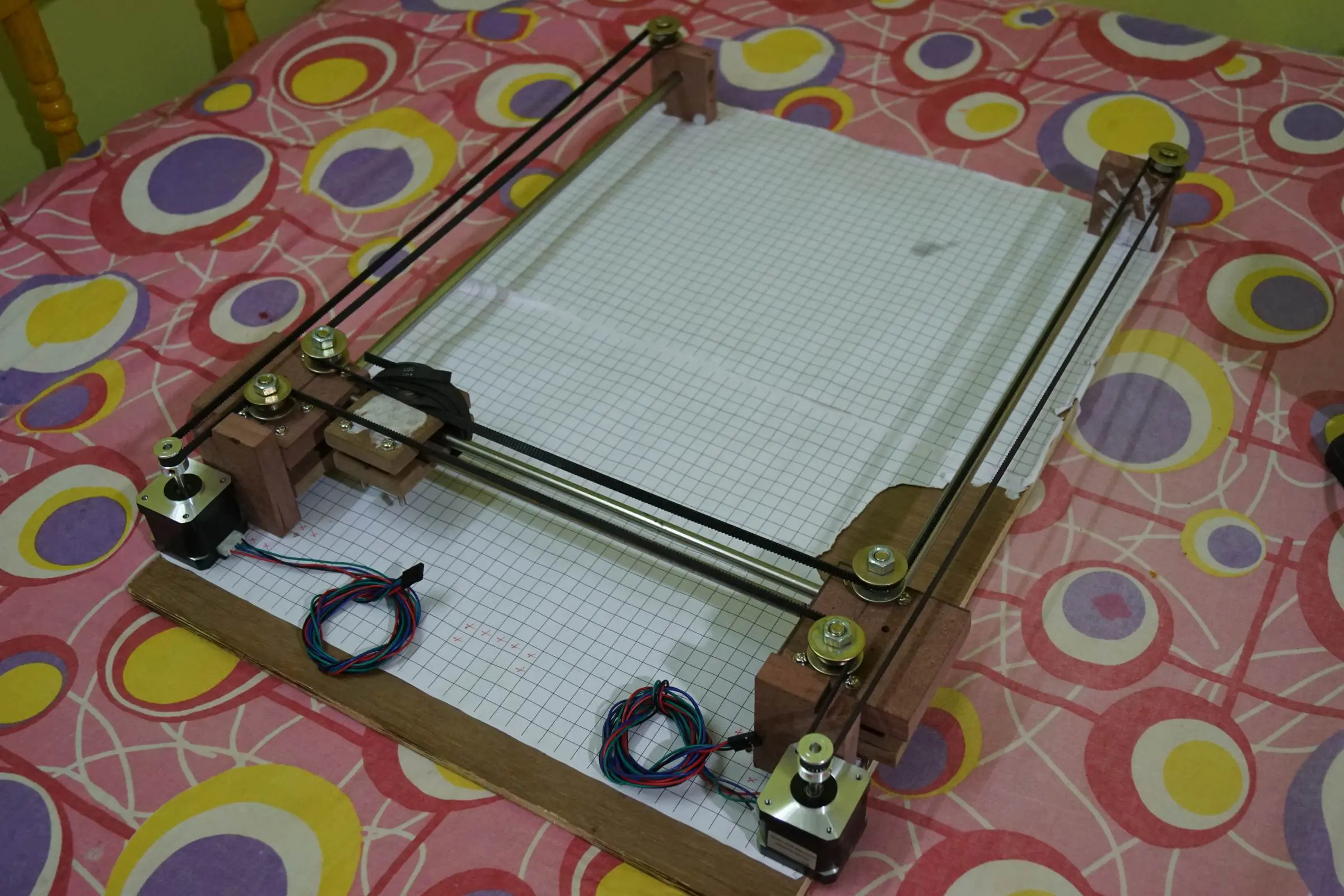

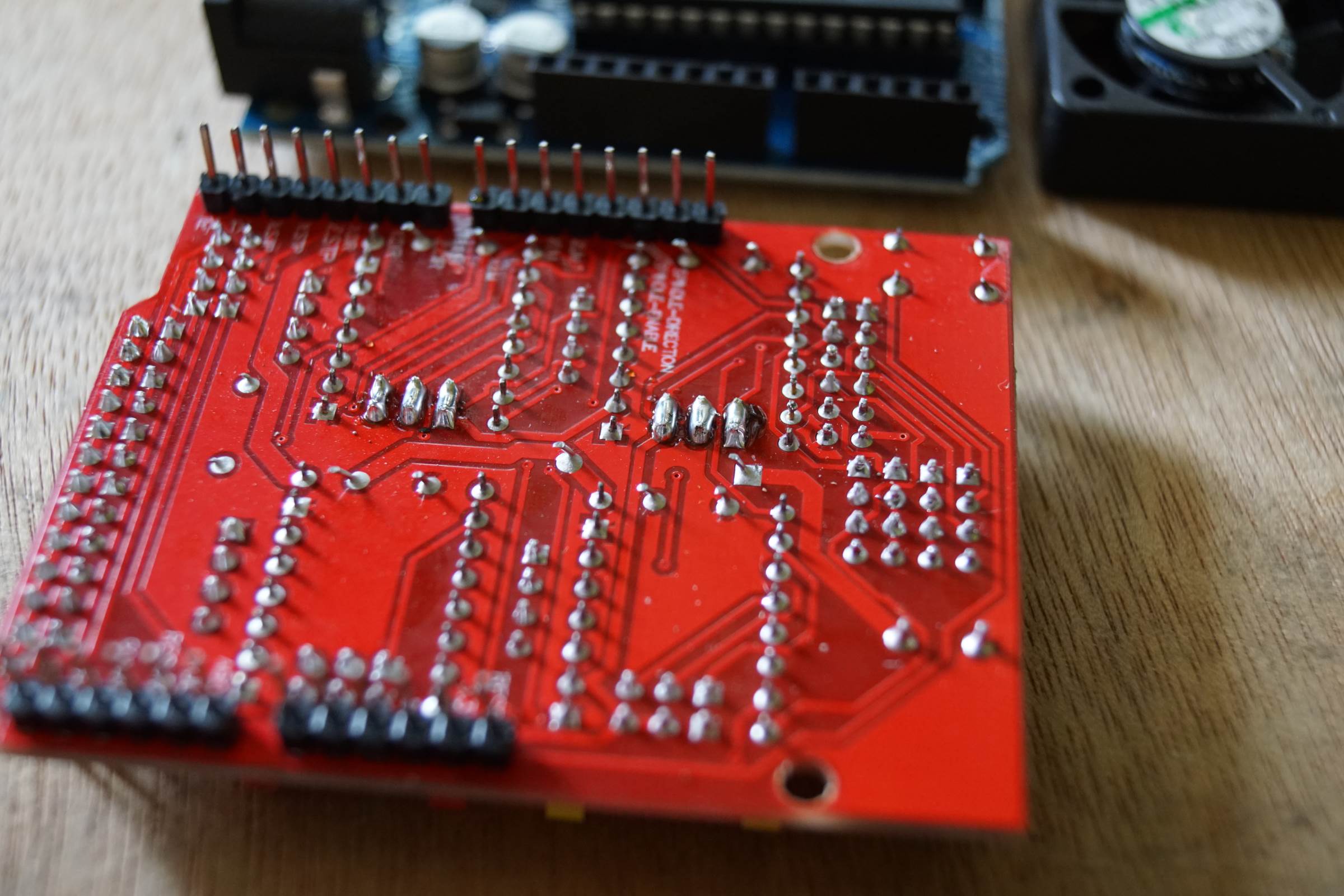
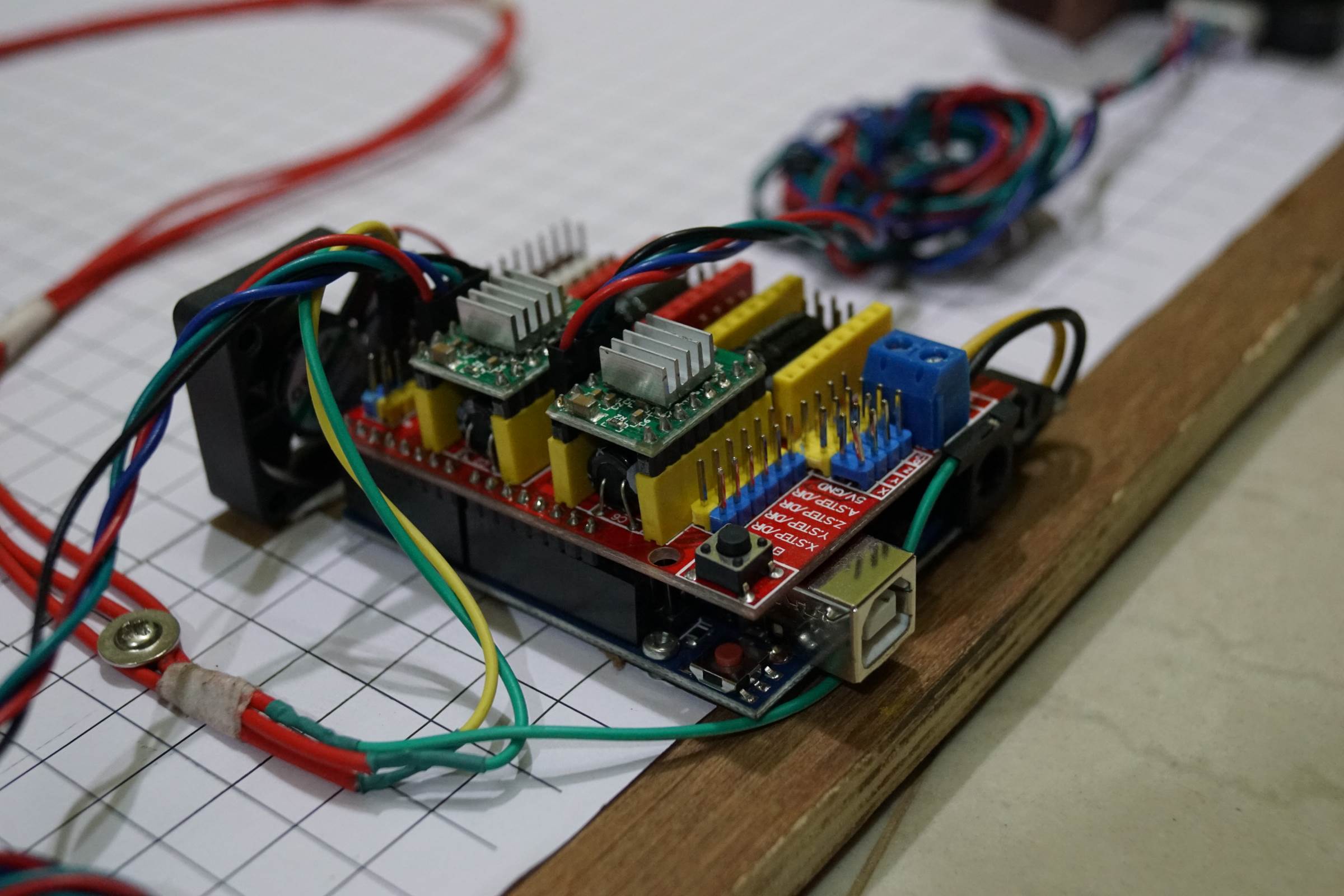
- Stepper Driver Micro Stepping Jumper Soldering for one/32 Microstepping

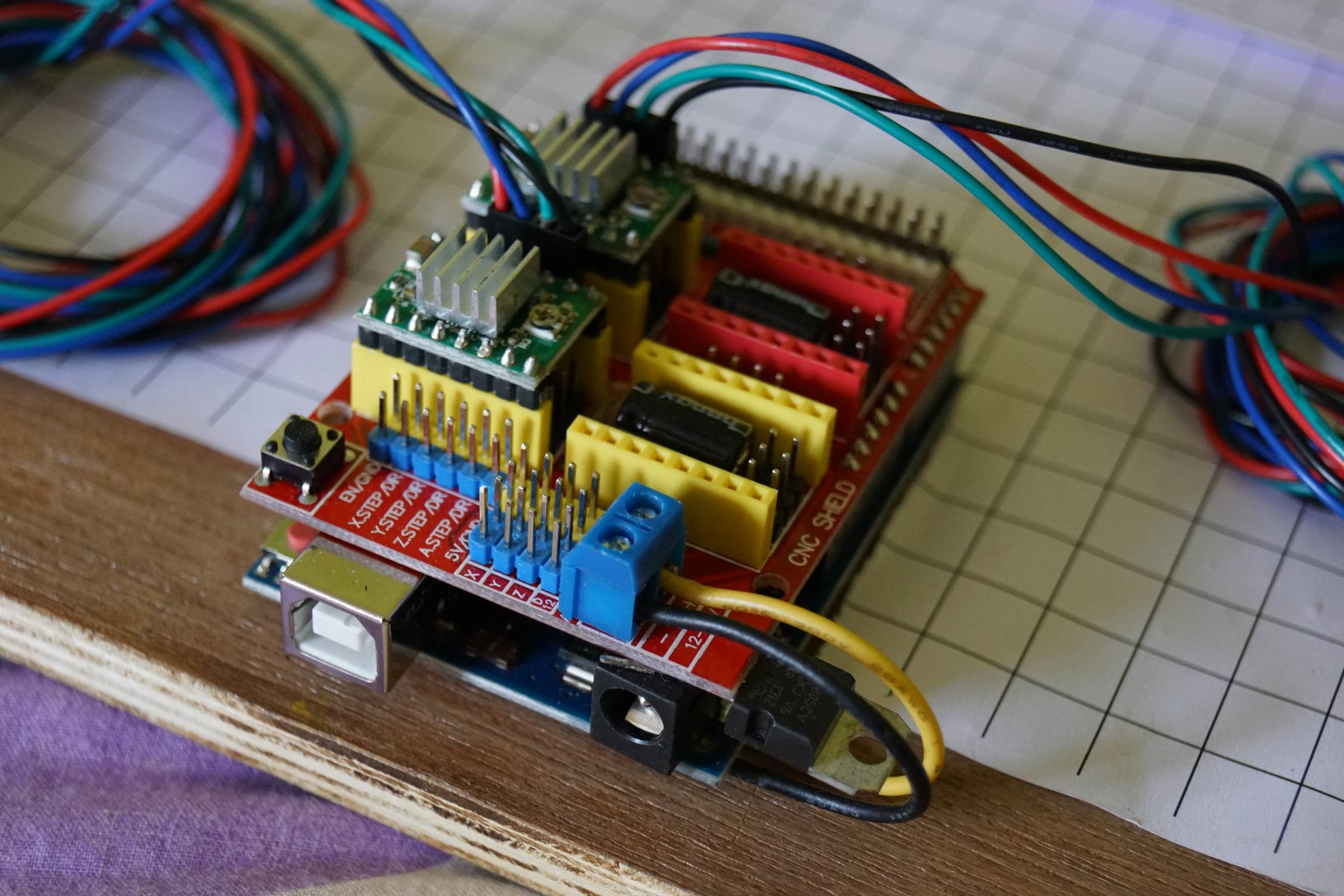
- A4988 Stepper Driver on CNC Shield V3, The Black and Yellowish Wires Provides 12V from Arduino Uno ( Soldered on Bottom Side) to CNC Shield

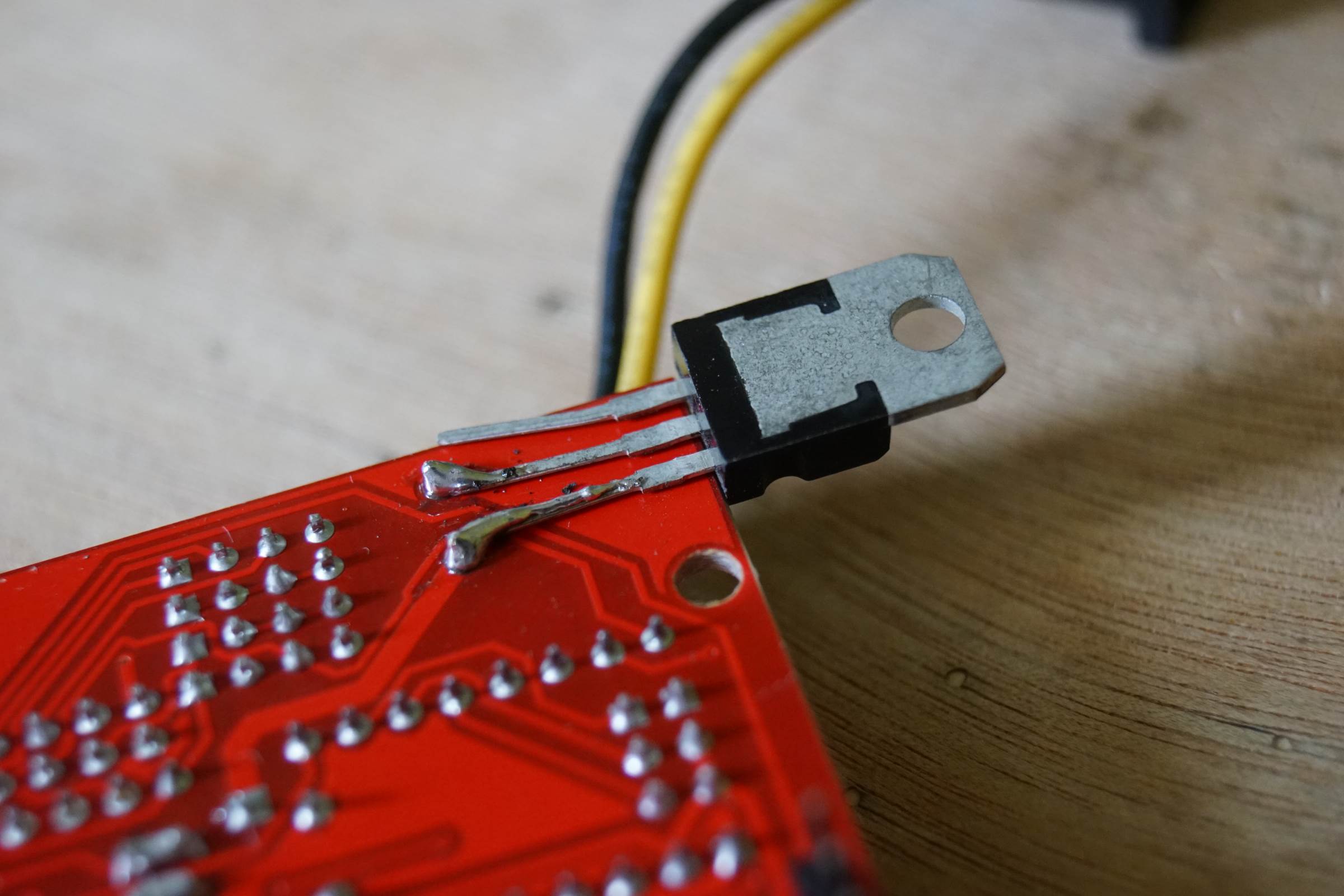
- LM7806 Soldered Directly on 12 Input to Provide 6V for Micro Servo

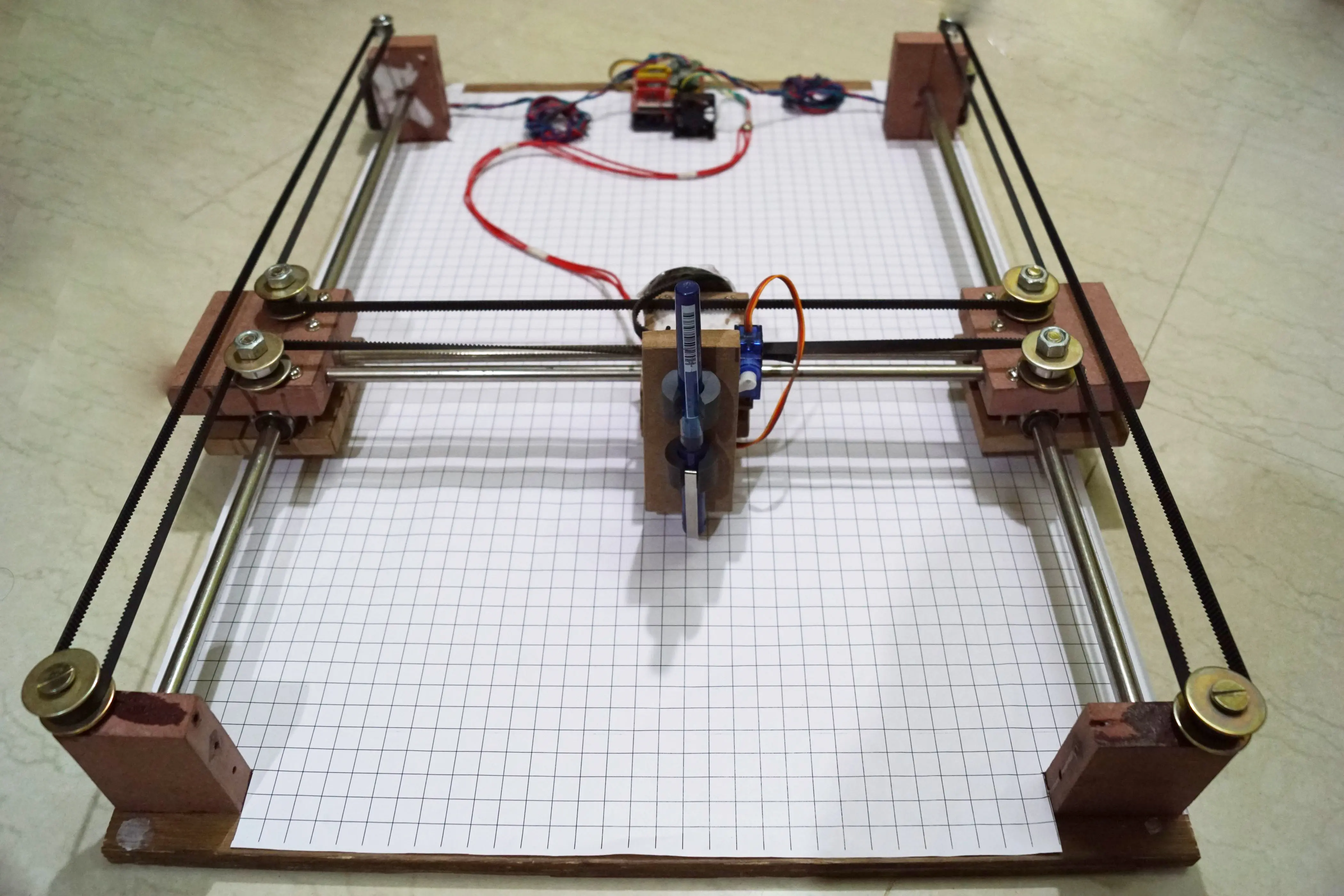
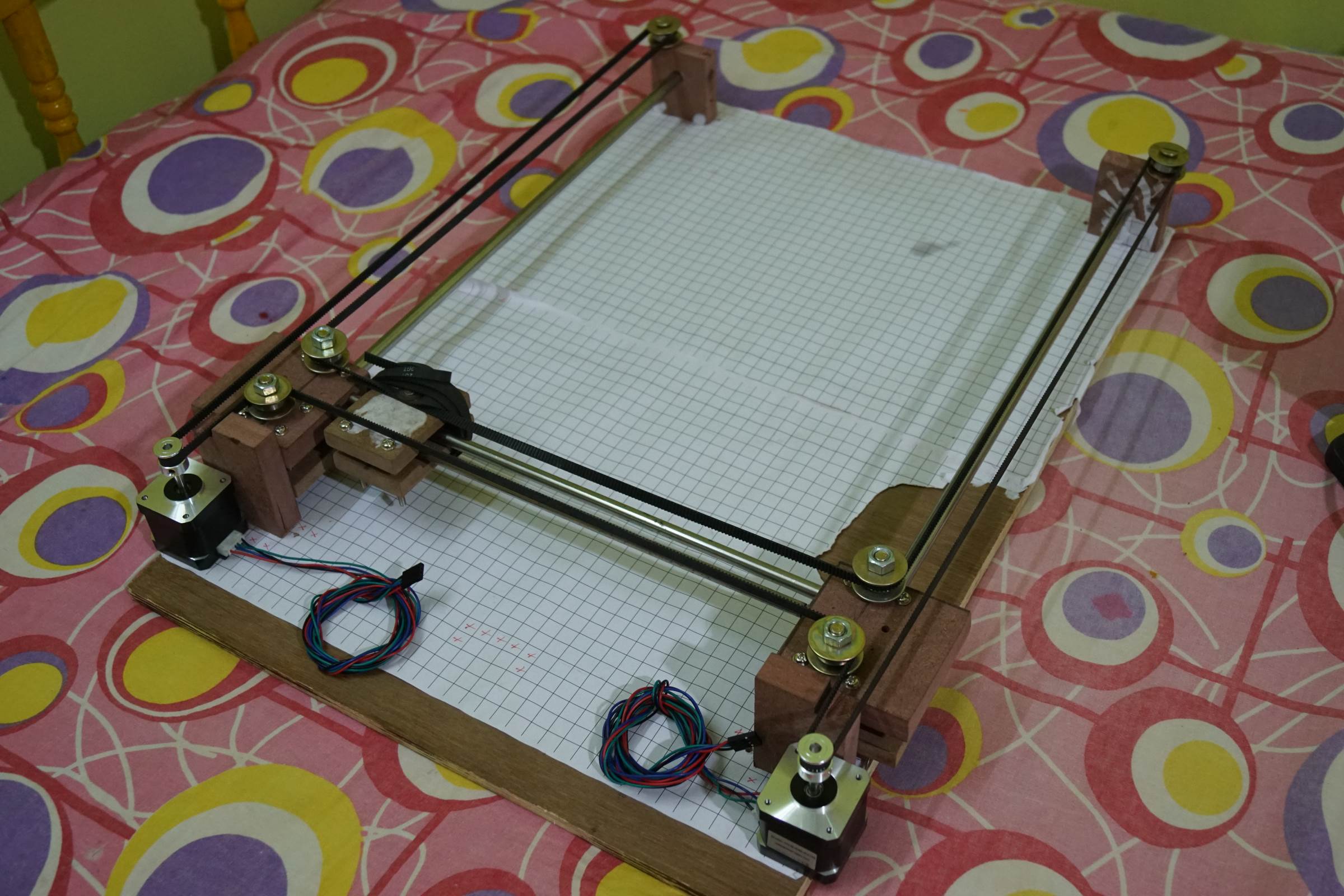
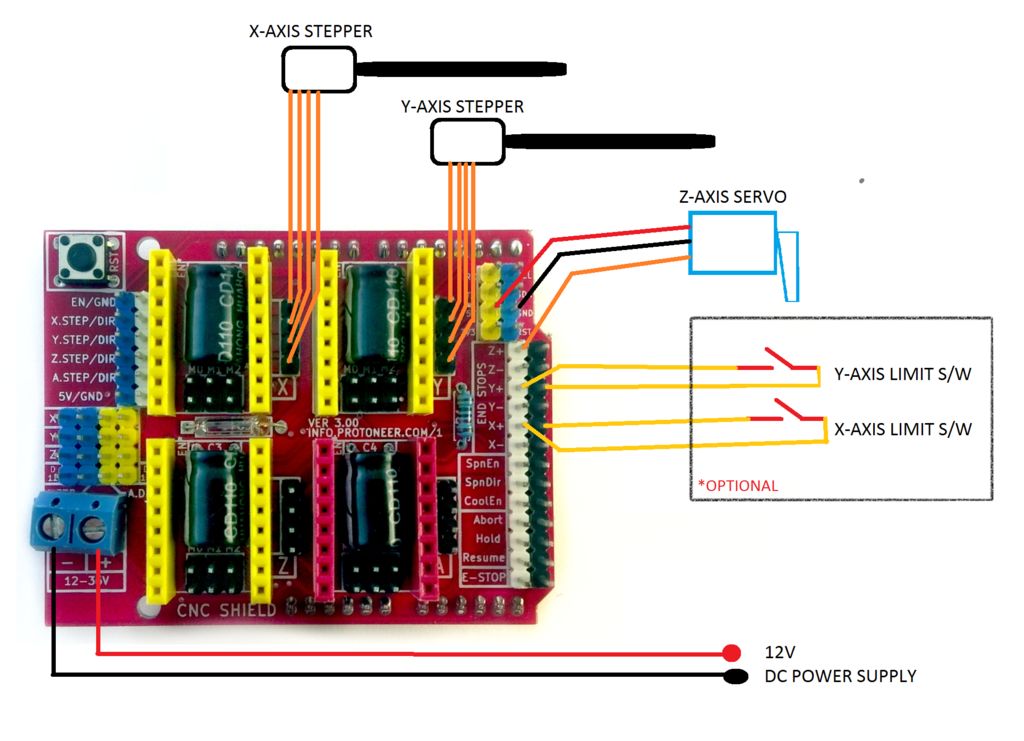
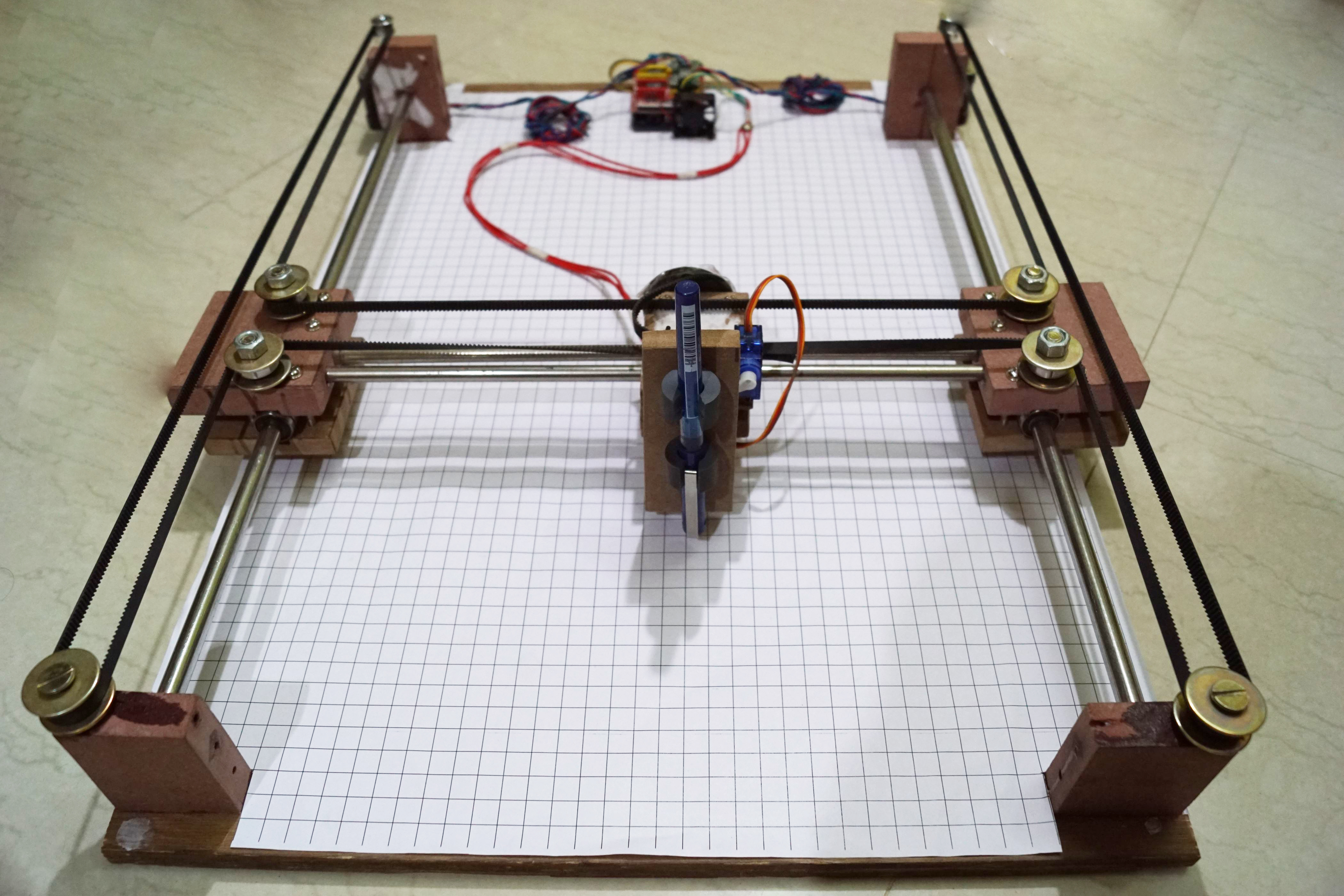
- Arduino CNC Cartoon Machine Complete Wiring
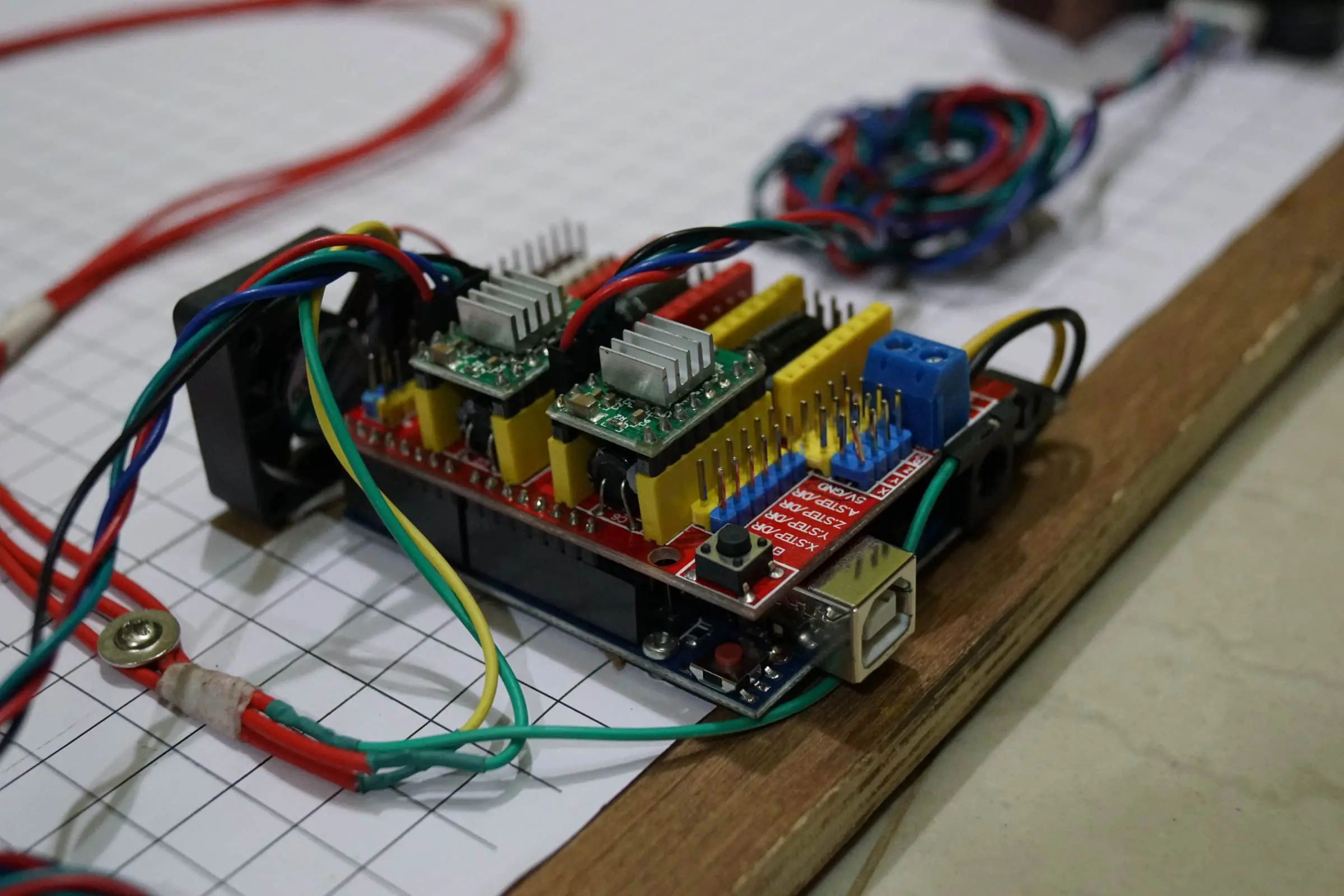
- Arduino Drawing Machine Schematics
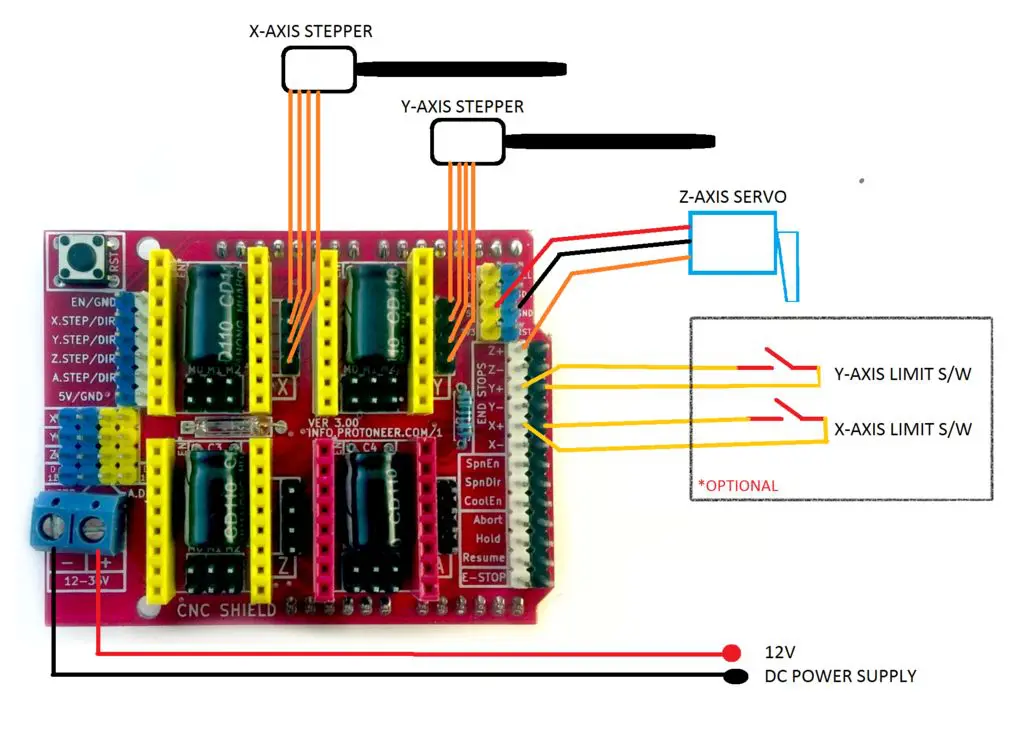
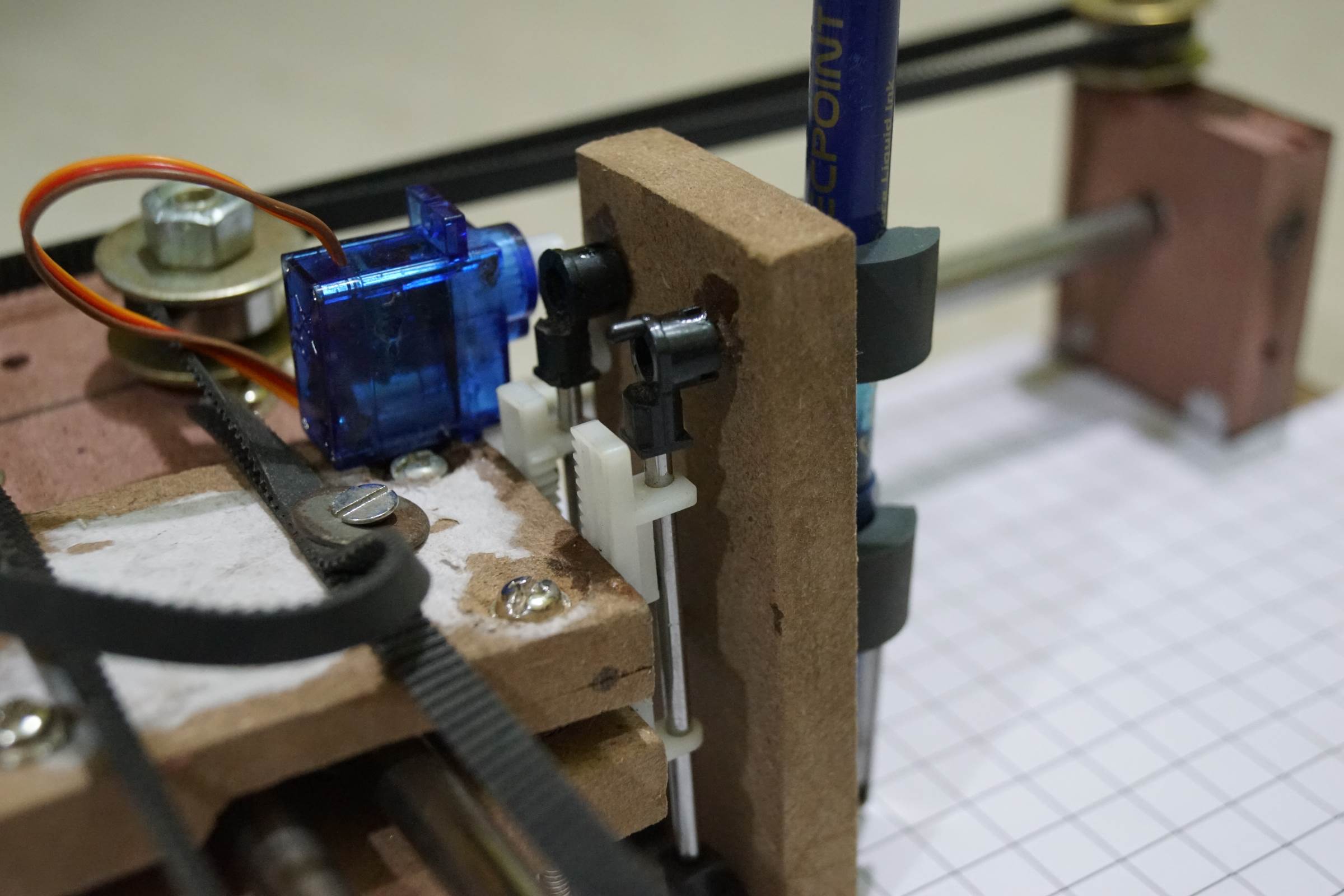
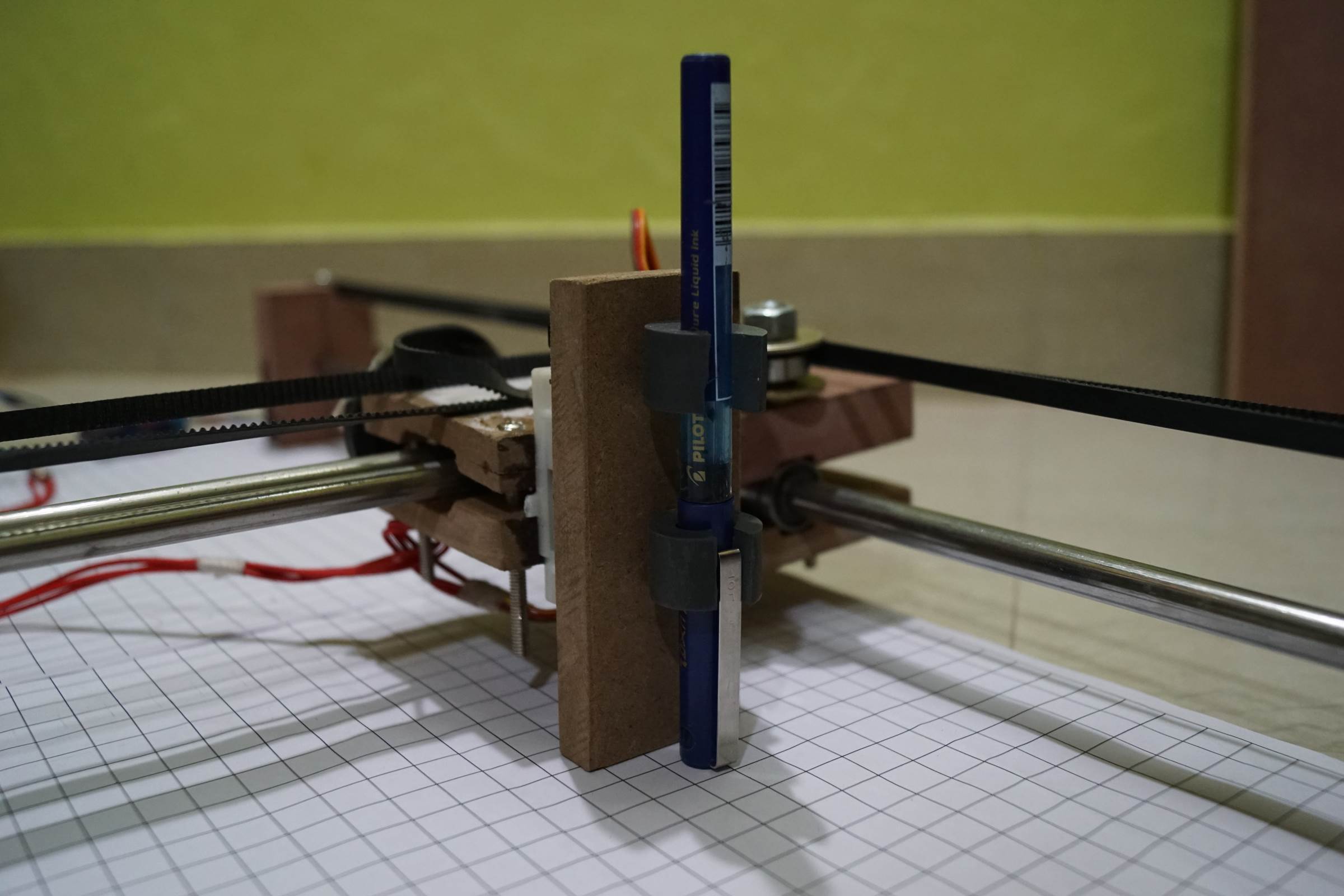
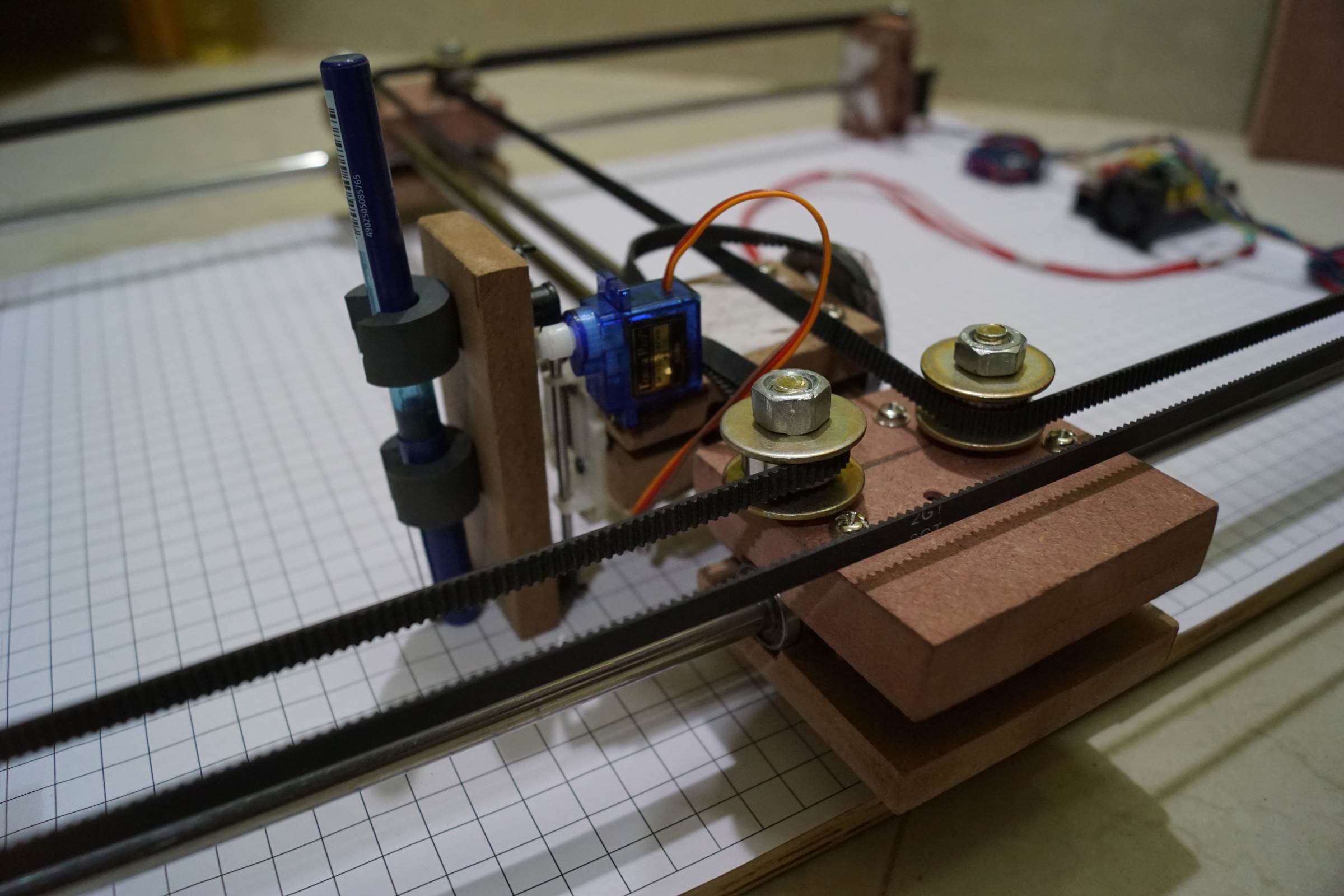
- Servo Motor Attachment for Pen Lifting in Arduino Cartoon Automobile

- Servo Motor Attachment for Pen Lifting in Arduino Drawing Machine

- Servo Motor Attachment for Pen Lifting in Arduino Drawing Machine
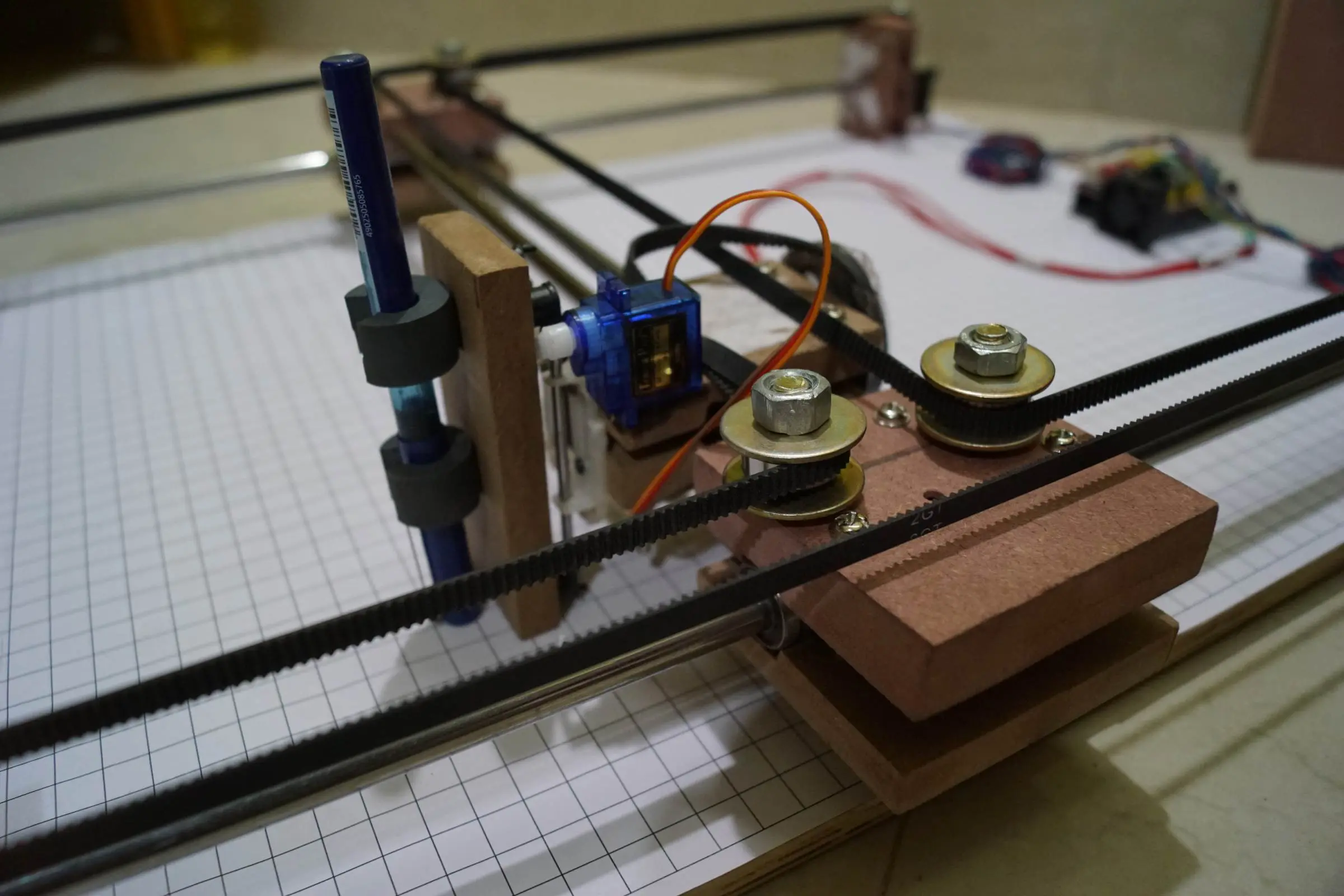
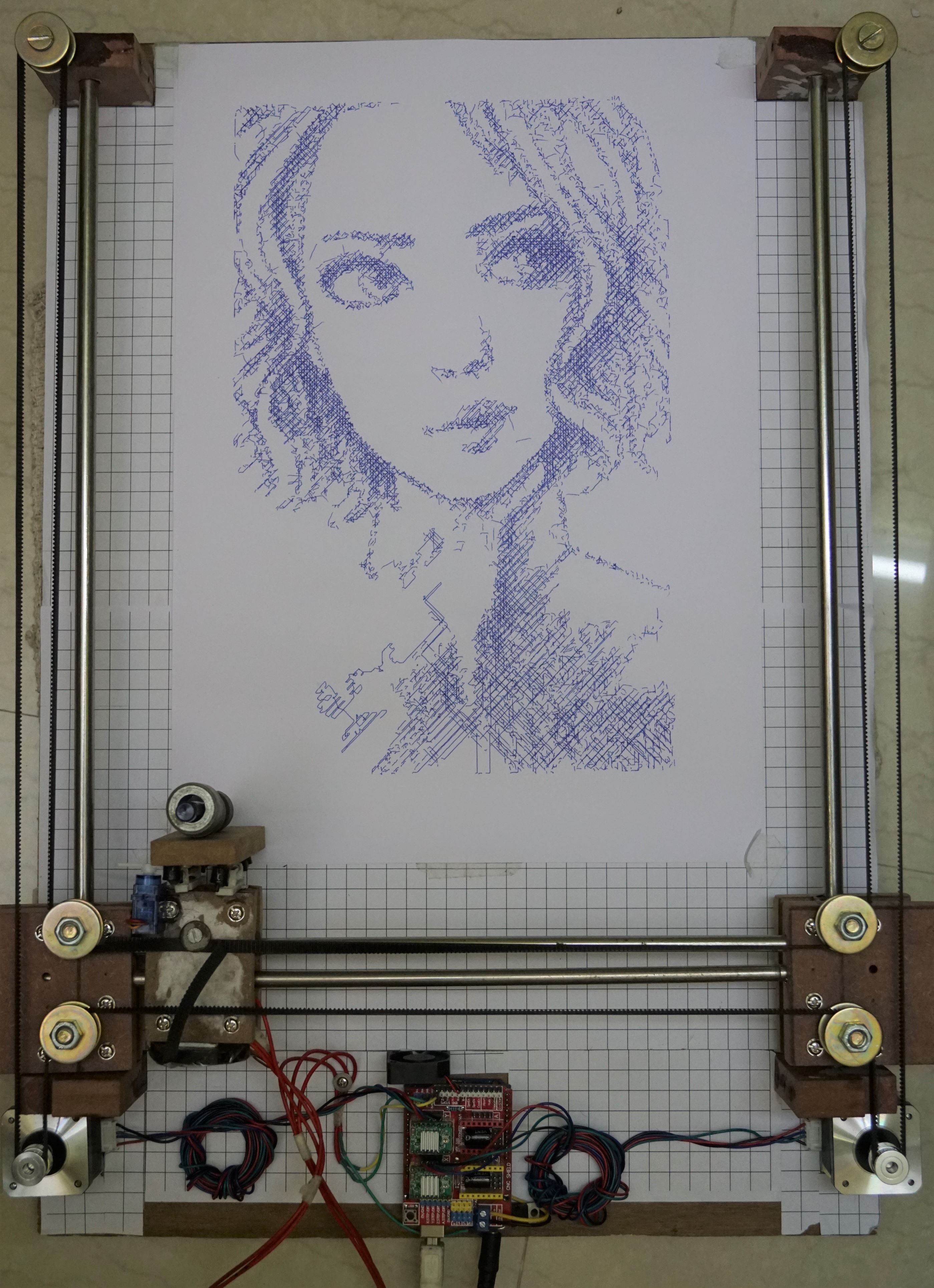
- Arduino Drawing Machine Working Output
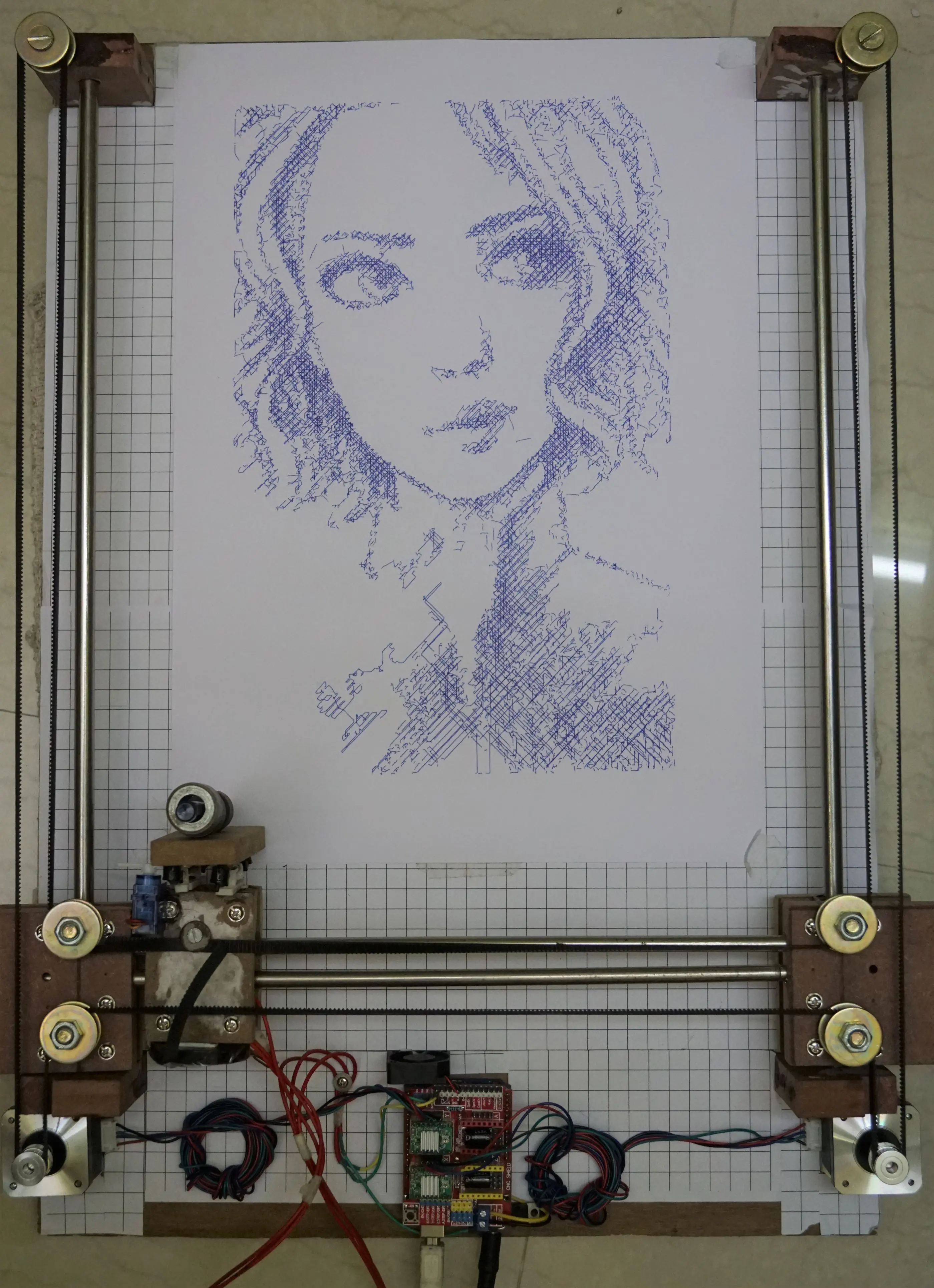
- Arduino Cartoon Machine Complete
Arduino Firmware Installation
This projection is using a modified version of GRBL 0.9i Firmware that is. I have modified to enable CoreXY configuration and also enabled servo motor performance on pin D11. The servo motor volition raise and lower the pen using Motorcar Lawmaking M03 and M05. (Will explain later in detail). So in Z-Axis, no Stepper Motor is required to pull the pen.
You Can Download my modified firmware from Git:https://github.com/arnabdasbwn/grbl-coreXY-servo
Grbl-coreXY-servo is a no-compromise, loftier performance, low-cost alternative to parallel-port-based motion control for CNC milling. Information technology volition run on a vanilla Arduino (Duemillanove/Uno) as long as it sports an Atmega 328p.
The controller is written in highly optimized C utilizing every clever feature of the AVR-chips to reach precise timing and asynchronous operation. Information technology is able to maintain up to 30kHz of stable, jitter-complimentary command pulses.
It accepts standards-compliant M-Code and has been tested with the output of several CAM tools with no problems. Arcs, circles and helical move are fully supported, too equally, all other primary M-Lawmaking commands. Macro functions, variables, and most canned cycles are not supported, but we retrieve GUIs can do a much better task at translating them into straight G-Lawmaking anyway.
Grbl-coreXY-servo includes full acceleration management with
alee. That means the controller will look upward to xviii motions into the future and program its velocities ahead to evangelize smooth acceleration and jerk-free cornering.
• Licensing: Grbl is free software, released nether the GPLv3 license.
After downloading you accept to flash the Arduino Uno with the firmware.
Hither are the Steps:
Annotation: Before starting, delete prior Grbl library installations from the Arduino IDE. Otherwise, you'll accept compiling issues! On a Mac, Arduino libraries are located in ~/Documents/Arduino/libraries/. On Windows, it'due south in My Documents\Arduino\libraries.
ane.Download from https://github.com/arnabdasbwn/grbl-coreXY-servo the ZIP File
• Unzip the download and you'll take a folder chosen
-coreXY-servo.
2.Launch the Arduino IDE
• Make certain you are using the most recent version of the Arduino IDE!
3.Load Grbl into the Arduino IDE every bit a Library
• Click the Sketch drib-down carte, navigate to Include Library and select
ZIP Library.
• Important: Select the Grbl folder inside the
-coreXY-servo-master folder, which merely contains the source files and an example directory.
• If yous accidentally select the .zip file or the wrong folder, you lot will need to navigate to your Arduino library, delete the mistake, and re-do Step iii.
4.Open the GrblUpload Arduino example
• Click the File downward-downwards menu, navigate to Examples->Grbl, and select GrblUpload.
five.Compile and upload Grbl-coreXY-servo to your Arduino
• Connect your Arduino Uno to your computer.
• Make sure your board is set to the Arduino Uno in the Tool->Lath card and the serial port is selected correctly in Tool->Series Port.
• Click the Upload, and Grbl-coreXY-servo should compile and flash to your Arduino! (Flashing with a programmer also works by using the Upload Using Programmer card command.)
Software Tools Installation
Nosotros need multiple software and plugins for generating art-work, editing and sending K-Lawmaking to the CNC using Serial COM Port. I will be discussing installation in Windows platform but you can notice all the software for Linux platform too. And so the software we will be using are:
>>> Inkscape
[ Will be used to edit vector graphics and likewise to generate vector graphics (.svg) from .jpg, .png and .dxf formats ]
• Download the latest stable 32bit/64bit version according to your OS from Inkscape.org
• Installation is pretty uncomplicated and straight frontward in Windows. In Linux you need to type some easy commands.
• Just practise a Next Next and software volition exist installed.
>>> JTP Light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation Tool Inkscape Plugin
[This Inkscape plugin will catechumen paths/drawing to K-Lawmaking for Vector Printing]
• Download the plugin from JTP Website
• Extract it using any skillful unzipping software.
• Put the contents of this .nil folder into the "inkscape\share\extensions" folder in installationdirectory.
• One time it is there information technology will show up under the "extensions" tab in Inkscape.
>>> Raster 2 Laser Yard-Code Generator
[This Inkscape plugin will convert paths/drawing to M-Lawmaking for Raster Printing]
• Download the plugin from my Git Hub Repository Raster ii Laser
• Extract it using whatever skillful unzipping software.
• Put the contents of this .zip folder into the "Inkscape\share\extensions" folder in installationdirectory.
• Once it is there it volition evidence up under the "extensions" tab in Inkscape.
>>> UGS Platform / UniversalGcodeSender
[ Will transport G-Codes from laptop to Arduino UNO via USB Serial Port]
• Download and install the version of Java listed on the download page co-ordinate to your OS and system configuration. Requires Java viii. Download Here
• Download UGS Platform UGS Download
• Extract it using any skillful unzipping software.
• In the extracted folders locate bin in the ugsplatform directory.
• On Windows run ugsplatform.exe or ugsplatform64.exe, on Linux or Mac OSX run ugsplatform.
• No need of whatever installation or build.
>>> Camotics
[ Will be used for visualizing G-Codes and simulation purpose]
• Download the latest version from Camotics
• Simple and fluid installation.
>>> Makelangelo Software
[Volition be used to generate monochrome pattern art piece of work from jpg, png and other formats that tin be printed by unmarried colour pen by CNC Drawing Auto]
• Download the Makelangelo Software from my Git Hub Repository Makelangelo-Software
• Extract it using any good unzipping software.
• Open the extracted binder and find Makelangelo10.jar file.
• Run the .jar file using Java viii you have installed in previous steps.
>>> Inkscape Template File
[This template will be used according to the paper feeded to the Drawing Machine and volition help in G-Lawmaking generation with verbal dimension]
• Download the template from my Git Hub Repository Inkscape-Template
• Extract information technology using any adept unzipping software.
• Open up the extracted folder and find Makelangelo10.jar file.
Processing from Existing JPG/PNG Image in Inkscape
• Open up Inkscape.
• Open up the template you have downloaded in previous step according to your paper size.
• Click on File -> Import then select the JPG or PNG file from your drive and click open.
• Resize and position the image co-ordinate to your page size.
• Image must exist within the boundaries of the page or Yard-lawmaking will not exist generated properly.
• Right Click on the prototype and select Trace Bitmap.
• Select whatsoever of the Three Option [ Experiment and Y'all will know the working] Brightness Cutoff, Border Detection, Colour Quantization.
• Change the threshold according to the details you desire in the drawing.
• Click on Update.
• Click OK and close the window.
• The Vector Bitmap will exist overlapping the original motion-picture show.
• Drag out the original motion-picture show and delete it. You are ready to generate 1000-code.
• At present SeeG-code Generation Step.
Processing from Custom Drawing in Inkscape
• Open up Inkscape.
• Open the template you take downloaded in previous pace according to your newspaper size.
• First drawing or writing text inside the piece of work area.
• Select all the objects by Ctrl+A shortcut.
• Group then together by Object -> Group from menu or by Ctrl+G shortcut.
• Then you have to convert object to path from card Path -> Object To Path or by shortcut Shift+Ctrl+C. [ Important Stride]
• Now Run intoChiliad-lawmaking Generation Step.
Generating Art Piece of work from Image in Makelangelo Software
• Open up Makelangelo Software running the .jar file.
• Click Open File and select the JPG/PNG file from your drive.
• Select the Conversion Style from the drop down carte. [ My fav is Crosshatch]
• Click ok.
• Click Save to file/SD Bill of fare and become to the location where you desire to save.
• Put your file name and select DXF R12 File Format .DXF.
• Now run Inkscape and open the saved .DXF file with default settings.
• Resize it according to your need.
• Now SeeG-code Generation Footstep.
Raster G-lawmaking Generation
• In raster style the machine will scan the whole drawing area from [0,0] till the cease line past line. [Raster way is slow and takes more time]. See the videos [Raster Drawing Girl'due south Face Video 1] [Raster Drawing Girl's Face up Video 2]
• After converting all objects to path from previous step you lot are gear up to generate your Grand-code.
• Now select all the paths that are inside the work expanse or utilise Ctrl+A.
• Click Extensions -> 305 Applied science -> Raster 2 Light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation G-code Generator.
• Give Export Directory Path.
• Give File Proper name.
• Enable Numeric Suffix.
• Resolution means number of lines per mm, increasing will increase drawing time.
• Play with the options beneath similar the RGB threshold.
• Set Engraving speed to 1500 or above.
• Select No Homing.
• Edit Light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation ON to M03 S255.
• Edit Laser OFF to M05 S0.
• Deselect Preview, if selected no G-code will exist generated.
• Click Utilise. Wait and Bask. You are Gear up to print now.
Vector Chiliad-code Generation
• In vector fashion the machine will scan the only the cartoon expanse where lines are there. [Vector way cartoon takes less time]. See the video [Vector Cartoon PowerPuff Girls Video ]
• Subsequently converting all objects to path from previous stride yous are fix to generate your Yard-code.
• Now select all the paths that are inside the work area or use Ctrl+A.
• Click Extensions -> Generate light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation One thousand-code -> J Tech Photonics Laser Tool.
• Requite Export Directory Path.
• Give File Name.
• Enable Numeric Suffix.
• Set All Units to mm.
• Set Laser speed to 1500 or to a higher place.
• Gear up Travel speed to 3000 or above.
• Select No Homing.
• Edit Laser ON to M03.
• Edit Laser OFF to M05.
• Deselect Preview
• Click Utilize. Wait and Enjoy. You are ready to Print now.
GRBL Configuration and Setting Upwardly Your Machine for the Get-go Time
Outset, connect to Grbl using the serial terminal of your selection.
Set the baud rate to 115200 as viii-Northward-1 (8-bits, no parity, and
chip.)
Once connected y'all should become the Grbl-prompt, which looks like this:
Grbl 0.9i ['$' for help]
Type $ and press enter to take Grbl print a help message. Yous should not run across whatever local echo of the $ and enter. Grbl should answer with:
[HLP:$$ $# $1000 $I $Due north $x=val $Nx=line $J=line $SLP $C $10 $H ~ ! ? ctrl-ten]
The '$'-commands are Grbl organization commands used to tweak the settings, view or modify Grbl's states and running modes, and starting time a homing cycle. The last four non-'$' commands are
control commands that can exist sent at
, no matter what Grbl is doing. These either immediately change Grbl's running
or immediately print a report of the important
data similar current position (aka DRO).
$$ – View Grbl settings
To view the settings, type $$ and press enter after connecting to Grbl. Grbl should respond with a list of the current arrangement settings, equally shown in the example below. All of these settings are persistent and kept in EEPROM, so if you power downward, these volition be loaded support the adjacent time you power up your Arduino.
$x=val – Save Grbl setting
The $x=val command saves or alters a Grbl setting, which can be washed manually by sending this command when connected to Grbl through a serial terminal program, but about Grbl GUIs will exercise this for you as a user-friendly characteristic.
To manually change e.thou. the microseconds step pulse choice to 10us you would type this, followed by an
:
$0=ten
If everything went well, Grbl will reply with an 'ok' and this setting is stored in EEPROM and will be retained forever or until you change them. You can check if Grbl has received and stored your setting correctly past typing $$ to view the organization settings again.
Grbl'southward default configuration is intentionally very generic to help ensure users can see successful movement without having to tweak settings. More often than not, the first thing y'all'll want to do is get your stepper motors running, normally without information technology connected to the CNC. Wire Grbl to your stepper drivers and stepper motors according to your manufacturer guidelines. Connect to Grbl through a serial terminal or one of many Grbl GUIs. Ship some G1 or G0 commands to Grbl. You lot should see your stepper motor rotating. If you are having trouble with your stepper motors, try the following:
• Ensure everything is wired and powered correctly per your stepper commuter manufacturer guidelines.
• If your steppers are mounted in your CNC already, ensure your axes movement freely and don't obviously bind. If you can't easily tell, try removing your steppers and check if they run under no load.
• Ensure your stepper motors and axes linear mechanisms are all tight and secure. Modest set screws on drivetrain components becoming loose is a very mutual problem. Re-tighten and effort applying some
–
thread locker (Loctite blue) if it continually loosens.
• For more difficult issues, attempt the procedure of elimination to quickly isolate the problem. Start past disconnecting everything from the Arduino. Test if Grbl is operating ok by itself. Then, add 1 thing at a fourth dimension and exam.
• If your steppers are powered and making a grinding noise when trying to move, try lowering the '$' acceleration and max rate settings. This sound is a sign that your steppers
losing steps and not able to go on up
too much torque load or going too fast.
• Grbl's default stride pulse settings cover the vast majority of stepper drivers on the market. While very uncommon, check these settings if yous are still experiencing problems or have a
.
Next, y'all will demand to make sure your machine is moving in the correct directions according to a Cartesian(XYZ) coordinate frame. Mount your stepper motors into your CNC, if you haven't already washed and then. Send Grbl some motion commands, such as G91 G0 X1 or G91 G0 X-ane, which volition move the x-axis +1mm and -1mm, respectively. Check all axes. If an centrality is not moving correctly, alter the $3 direction port mask setting to invert the direction.
If you are unfamiliar with how coordinate frames are
on CNC machines, see this great diagram by LinuxCNC. But keep in mind that motions are relative to the tool. So on a typical CNC gantry router, the tool will motion rather than the fixed table. If the x-axis is aligned positive to the right, a positive motion command will motility the tool to the right. Whereas, a moving tabular array with a stock-still tool will motion the table to the left for the same
because the tool is moving to the right relative to the table.
Finally, tune your settings to become close to your desired or max performance. First by ensuring your $100,$101, and $102 axes step/mm settings are right for your setup. This is dependent on your stepper increments, micro steps on your driver, and mechanical parameters. There are multiple resources online to evidence you lot how to compute this for your particular
if your auto manufacturer has not supplied this for you. Tweak your $11x dispatch and $12x max rate settings to improve performance. Set to no greater than lxxx% of absolute max to account for inertia and cutting forces. Set your $13x max travel settings if you plan on using homing or soft limits. It's recommended to enter something approximately close to actual travel now to avoid problems in the future.
At this bespeak, you're pretty much ready to get going! Grbl can at present move your CNC machine and run G-lawmaking jobs. If yous need to add together more than features, such as limit switches for homing or hard limits or spindle/laser control. In that location are other Wiki pages to help you that. Good luck and have fun!
Hither is my GRBL Setting$0 = 10 (step pulse, usec)
$one = 25 (step idle delay, msec)
$two = 0 (pace port capsize mask:00000000)
$three = 0 (dir port invert mask:00000000)
$4 = 0 (stride enable invert, bool)
$5 = 0 (limit pins invert, bool)
$6 = 0 (probe pin invert, bool)
$ten = 3 (status study mask:00000011)
$11 = 0.010 (junction deviation, mm)
$12 = 0.010 (arc tolerance, mm)
$13 = 0 (report inches, bool)
$20 = 0 (soft limits, bool)
$21 = 0 (hard limits, bool)
$22 = 0 (homing cycle, bool)
$23 = 0 (homing dir invert mask:00000000)
$24 = 25.000 (homing feed, mm/min)
$25 = 500.000 (homing seek, mm/min)
$26 = 250 (homing debounce, msec)
$27 = 1.000 (homing pull-off, mm)
$100 = fourscore.000 (x, step/mm)
$101 = fourscore.000 (y, stride/mm)
$102 = 80.000 (z, step/mm)
$110 = 50000.000 (ten max rate, mm/min)
$111 = 50000.000 (y max charge per unit, mm/min)
$112 = 50000.000 (z max charge per unit, mm/min)
$120 = 5000.000 (x accel, mm/sec^2)
$121 = 5000.000 (y accel, mm/sec^two)
$122 = 30.000 (z accel, mm/sec^ii)
$130 = 310.000 (x max travel, mm)
$131 = 450.000 (y max travel, mm)
$132 = 200.000 (z max travel, mm)
Happy Making
Liking this content ? Please Donate to support this website ! 😇
Source: https://www.arnabkumardas.com/topics/cnc/how-to-make-an-arduino-drawing-machine/
Posted by: covarrubiasdond1949.blogspot.com















0 Response to "How To Make A Cnc Drawing Machine At Home"
Post a Comment